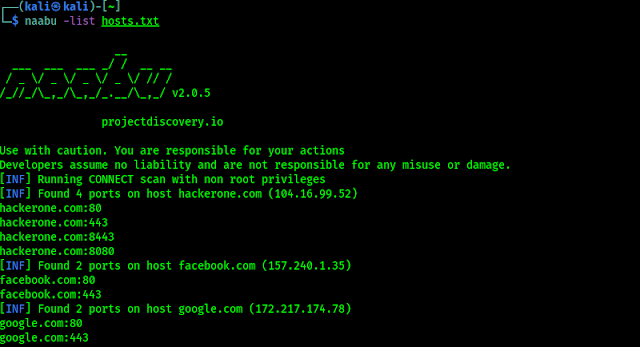
Most Secure Decentralized Cloud Drive on Linux
Nowadays can we imagine that we load a large file on our thumb drive and go to our friend’s home to give the file? No this is the era of cloud. We can easily store that file on our cloud storage and share it with our friend. Cloud storage solves a lot of problems.
But every innovation had their own problems, many cloud storage services sell our data or various private information to show ads. They also know our behavior and much more about us, they sell our data to maintain their profit. If we need good service and privacy then we need to away from free services because “If you are not paying for it, you’re not the customer; you’re the product being sold.“
It is very difficult to find a trusted and good cloud drive for us. We are Linux users we also need a well optimized Linux application to use cloud storage. Here we have Internxt.
Internxt and it’s Features
Internxt Drive is a zero-knowledge, decentralized & encrypted cloud storage service with Internxt, everything we store or transfer is encrypted before leaving our device. The price of using Internxt is very minimal. Even with a free account we can store 10 GB data with all the premium features.
The key features of Internxt is following:
- Fully encrypted cloud service.
- Safe and secure cloud service.
- Free private cloud storage.
- Best alternative to Google Drive, DropBox, and Microsoft One Drive.
- Best secure drive alternative.
- Best drive service for privacy and security.
- Zero-trust cloud service.
- World’s most secure cloud service.
How to Install Internxt on Linux
Internxt is cross platform. That means we can use it on every kind of operating system like, Windows, Mac, Linux, Android and iOS. But for being a Linux specific website we are just gonna show how to install Internxt on our Linux. Here we have used Kali Linux but the same process can be followed for other Debian based Linux distributions as Ubuntu, Elementary OS, Linux Mint etc.
First of all we need to go to the Internxt Drive web page, Then we need to click on Download for Linux, as shown in the following screenshot:
Now we need to save the .deb file of Internxt, as shown in the following screenshot:
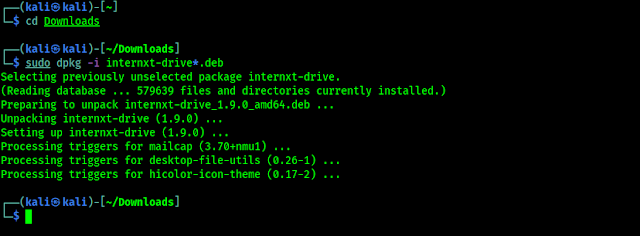
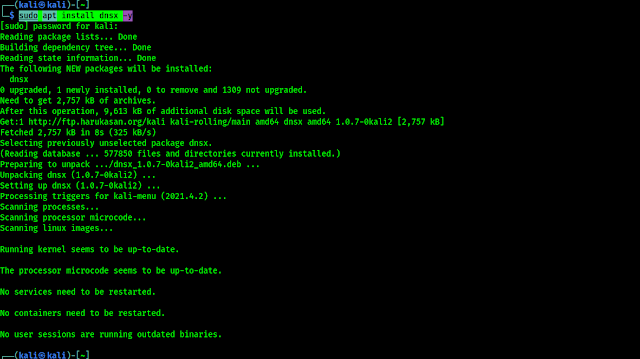
After the download is complete we can see the deb file is saved on our Downloads directory. So Here we need to open our terminal window and run following command to change our directory to Downloads:
Then we need to run following command to install Internxt Linux Desktop application:
As we can see in the following screenshot:
After the installation process s done we can see Internxt on our Application menu:
Now we can use Internxt directly from our Linux system by logging in to the application a new directory usually home/Internxt will be created on our system which will be synced with the Internxt Drive application.
Special Notes
Before buying the service we should try it using a free account which gives us 10GB space with all premium features. Internxt didn’t charges a lot. We can check the pricing here. It is worth every penny, but here we have an extra offer for our readers. Our readers can get extra 20% discount on all Internxt Annual plans by using our coupon code KALILINUXIN.
We are using Internxt personally, and loved it so much. Cloud is the future. We must be a part of this from now. Internxt is going for web3 for better anonymity.
 |
| Image Credit: Twitter |
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.