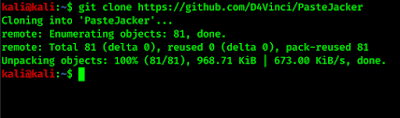
Airgeddon is a multi-featured tool for penetration testing on WiFi system or wireless networks. This all-in-one WiFi auditing tool is written in bash by v1s1t0r1sh3r3.
Key-Features of Airgeddon
Airgeddon has so much features for WiFi hacking. They are following:
- Interface mode switcher (Monitor-Managed) keeping selection even on interface name changing.
- DoS over wireless networks using different methods (mdk3, mdk4, aireplay-ng). “DoS Pursuit mode” available to avoid AP channel hopping (available also on DoS performed on Evil Twin attacks).
- Full support for 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz bands.
- Assisted WPA/WPA2 personal networks Handshake file and PMKID capturing
- Cleaning and optimizing Handshake captured files.
- Offline password decrypting on WPA/WPA2 captured files for personal networks (Handshakes and PMKIDs) using dictionary, bruteforce and rule based attacks with aircrack, crunch and hashcat tools. Enterprise networks captured password decrypting based on john the ripper, crunch, asleap and hashcat tools.
- Evil Twin attacks (Rogue AP)
- Only Rogue/Fake AP mode to sniff using external sniffer (Hostapd + DHCP + DoS).
- Simple integrated sniffing (Hostapd + DHCP + DoS + Ettercap).
- Integrated sniffing, sslstrip2 (Hostapd + DHCP + DoS + Bettercap).
- Integrated sniffing, sslstrip2 and BeEF Browser Exploitation Framework (Hostapd + DHCP + DoS + Bettercap + BeEF).
- Captive portal with “DNS blackhole” to capture wifi passwords (Hostapd + DHCP + DoS + Dnsspoff + Lighttpd).
- Optional MAC spoofing for all Evil Twin attacks.
- WPS features
- WPS scanning (wash). Self parameterization to avoid “bad fcs” problem.
- Custom PIN association (bully and reaver).
- Pixie Dust attacks (bully and reaver).
- Bruteforce PIN attacks (bully and reaver).
- Null PIN attack (reaver).
- Known WPS PINs attack (bully and reaver), based on online PIN database with auto-update.
- Integration of the most common PIN generation algorithms (ComputePIN, EasyBox, Arcadyan, etc.).
- Offline PIN generation and the possibility to search PIN results on database for a target.
- Parameterizable timeouts for all attacks.
- Enterprise networks attacks
- Fake AP using “smooth” and “noisy” modes capturing enterprise hashes and plain passwords.
- Custom certificates creation.
- WEP All-in-One attack (combining different techniques: Chop-Chop, Caffe Latte, ARP Replay, Hirte, Fragmentation, Fake association, etc.).
- Compatibility with many Linux distributions (see Requirements section).
- Easy targeting and selection in every section.
- Drag and drop files on console window for entering file paths or autocomplete using tab key on every path input for easier use.
- Dynamic screen resolution detection and windows auto-sizing for optimal viewing.
- Controlled Exit. Cleaning tasks and temp files. Restoring nftables/iptables after an attack that require changes on them. Option to keep monitor mode if desired on exit.
- Multilanguage support and autodetect OS language feature (see Supported Languages section).
- Help hints in every zone/menu for easy use.
- Auto-update. Script checks for newer version if possible.
- Docker image for easy and quick container deployment. Use already built image on Docker Hub or build our own.
- Http proxy auto detection for updates.
- Wayland graphic system supported (not only X window system).
- Tmux support for headless (systems without X window) environments.
- Multiple configurable options based on fallback substitution variables options system which allow to configure many enhancements like enable/disable colors, 5Ghz band, auto updates, hint printing, etc.
- Full compatibility with iptables and nftables with autodetection and possibility to force iptables by setting an option.
- Available plugins system to let the community create their own content in an easy and flexible way using the created function hooking system. More info at Plugins System section.
Installing Airgeddon on Kali Linux
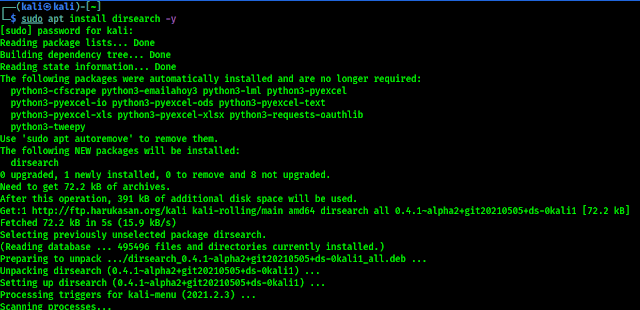
We can install airgeddon from it’s GitHub repository by cloning/downloading the repository. But in Kali Linux 2021.1 update this tool is added to Kali Linux repository. We can install it by simply using apt-get install command from any version of Kali Linux:
sudo apt-get install airgeddon
This command will install airgeddon on our Kali Linux system. The above command will prompt for root password and disk space permissions. After that this airgeddon and it’s essential requirements will be installed.
Airgeddon also requires some additional tools to use all it’s features. To install them all on our Kali Linux we use following one liner command:
sudo apt install bettercap isc-dhcp-server hostapd hostapd-wpe udhcpd mdk4 hcxdumptool lighttpd hcxtools -y
Now we can use airgeddon on our system.
Requirements for Airgeddon
- WiFi networks for testing.
- WiFi adapter that supports monitor mode & packet injection [List].
Using Airgeddon on Kali Linux
Now we can run following command to run airgeddon on our Kali Linux system.
sudo airgeddon
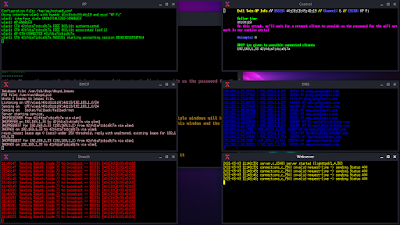
Then airgeddon will open in front of us as shown in the following screenshot:
After it will ask to check for all the tools installed or not, we need to press ↵ Enter to continue.
In the above screenshot we can see that we have all the tools. Now we plugin our external USB WiFi adapter that supports monitor mode and packet injection. Then we again need to press ↵ Enter again to continue.
Here we can see the list of interfaces on our system, as the following screenshot.
In our case our wlan1 interface supports monitor mode and packet injections, so we press 5 and hit ↵ Enter. This will tell airgeddon that we are going to work with that interface.
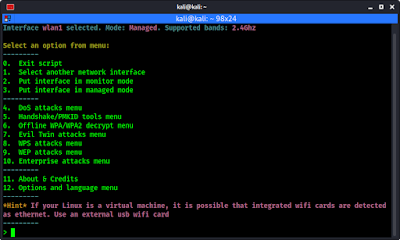
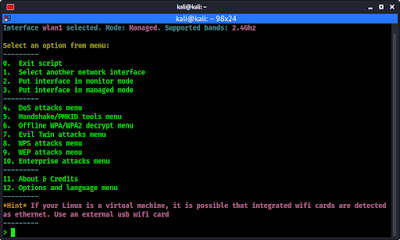
After that we got the main menu of airgeddon script.
Here at the top we can see our interface name and mode. The mode is ‘managed’ we need to change it to ‘monitor’ mode. Here everything is very clear and simple.
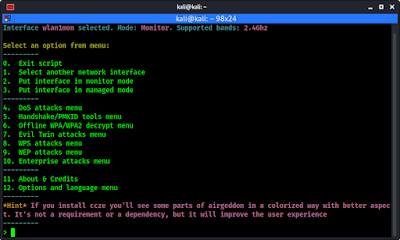
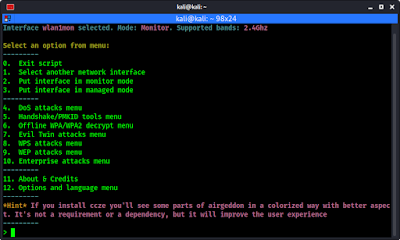
We can use option 2 to change the interface mode to monitor. We press 2 and ↵ Enter.
In the above screenshot we can see that our interface is changed from wlan1 to wan1mon and the mon is for monitor mode.
Now we can perform attacks using this script. For example here we demonstrate handshake capturing and evil-twin attacks using airgeddon on Kali Linux.
Capture and Crack Handshake File using Airgeddon
For an example first we capture handshake of a wireless network. Now what is handshake file? We know if we previously used a WiFi network using password and the password isn’t changed then we can easily connect to the network because of the handshake file. This file stores the password with encryption.
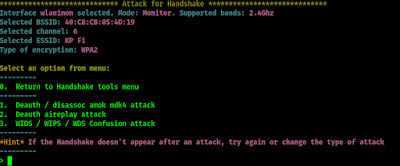
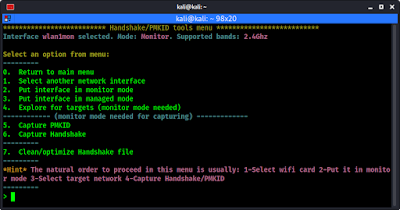
To perform handshake capture attack we enter in the handshake tools menu by pressing 5 and ↵ Enter. Then the handshake menu comes in front of us as the following screenshot.
Here the option number 6 is for capture the WiFi handshake. So we press 6 and hit ↵ Enter.
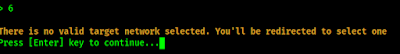
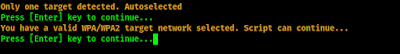
We did not choose any network, so airgeddon is redirect us to select a target WiFi network. We need to press ↵ Enter to continue.
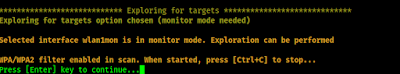
Here we explore for target WiFi network. We can start the attack by pressing ↵ Enter, when we think we have found our target network we can press CRL+C to stop searching.
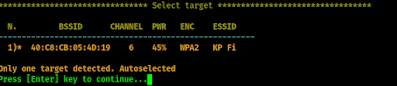
Here we can see that a another window is opened to search for networks. We can see that we have only target. So we can stop the search by pressing CTRL+C. Then it will show the list of targets.
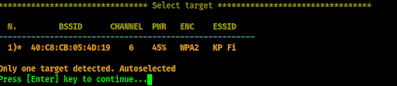
As we told, we have only one WiFi network (we live in a remote area). That’s why airgeddon automatically select this. Otherwise we need to select the number of the WiFi network to select it.
We press ↵ Enter to continue.
Now airgeddon got a valid target it it asks to continue the handshake capture. We again press ↵ Enter to continue.
Then airgeddon again prompts for the methods to capture the handshake file, as we can see in the following screenshot.
For an example we choose the deauth attack (No. 1). So we choose number 1 and press ↵ Enter.
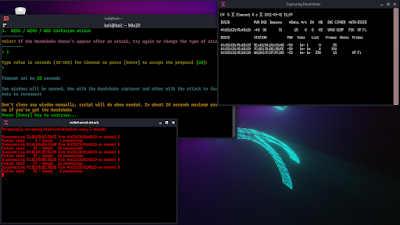
Here we need to type of the value in seconds. We can simply press ↵ Enter to left it on it’s default value, which is 20. Then it show us some advises as we can see in the following screenshot:
We can see in the above screenshot that the tool is going to capture the handshake. It also advice us to not close the windows manually during handshake capturing. We will know when airgeddon capture the handshake file. We need to press ↵ Enter to continue.
Then we can see some terminal window is opened in front of us in the following screenshot. We should not close them.
To clear some things here airgeddon sending de-authentication packets to the network, then all the WiFi users will disconnect for some seconds for the flood. Whenever the devices trying to connect back the WiFi network airgeddon will capture the handshake file.
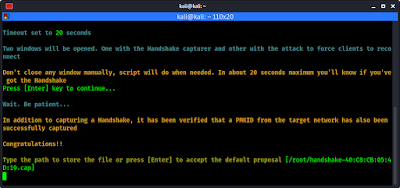
After successfully capturing the handshake file these will close automatically, and show us a congratulations message. It also asks where we want to save our handshake file. The default is under /root/handshake**.cap as we can see in the following screenshot.
Here also we goes with the default by just pressing ↵ Enter. Then the handshake file is stored successfully on the root folder. Handshake capturing is complete now. We can press ↵ Enter again to back in the menu.
We can press 0 and ↵ Enter to return to the main menu.
Our captured handshake file is stored on /root/ directory. We can see it by opening our thunar file manager with root permission (sudo thunar).
We can crack the handshake file in various way. We can use airgeddons menu Airgeddon > Offline WPA/WPA2 decrypt menu > Personal > (aircrack + crunch) Bruteforce attack against Handshake/PMKID capture file. We also can use aircrack-ng or some other brute-forcing tool. There are also some online tools are available.
Evil Twin Attack using Airgeddon
We can do a lot of attacks using airgeddon. Evil twin is one of them. In this attack we create a copy of our target access point and whenever the user of the access point try to connect with our fake access point with their access point’s password we got it. But why they do it?
Because we continuously send de-authentication packets to the target access point (AP), so that the user will not able to connect with the original AP, and got trapped.
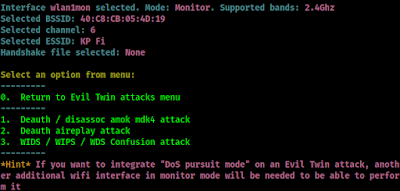
First of all we set the mode to monitor. Then we choose ‘Evil Twin attacks menu’ by pressing 7 and ↵ Enter.
Here we need to explore for the target by typing 4 as we did in the previous attack. We got auto-selected because we have only one target nearby.
Then we click ↵ Enter to continue. We get back to the ‘Evil Twin attacks menu’. Here we choose 9 for captive portal attack.
Now here we choose option 2 for ‘Deauth aireplay attack’.
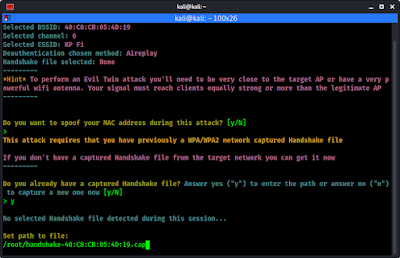
Airgeddon will ask us some question. First it will ask that if we want to integrate “DoS pursuit mode”. The default is N for no, we also know that our AP will not change the channel in this case, so we press ↵ Enter to keep it default. Then it will ask if we want to spoof our mac address. We also goes with default (that is N).
Now airgeddon will ask us that have we captured the handshake of this access point. In our above attack we had captured it. So we choose Y for yes. Then it will prompt for the location of the handshake file, and we provide it, as we can see in the following screenshot:
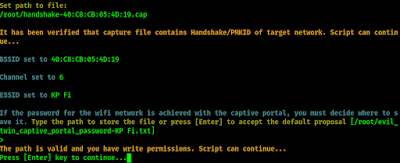
Then it asks the location where the saved password will stay in a text file. Default location is under /root/ directory. We again goes with the default by just pressing ↵ Enter.
We can see in the above screenshot that our path is valid and we can move forward by pressing ↵ Enter.
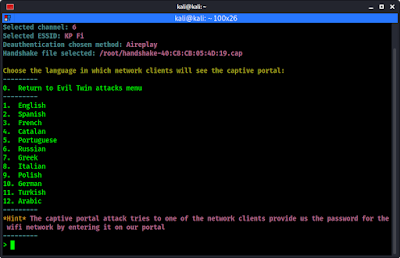
In the next step airgeddon will create a phishing page and asks us for it’s language, as we can see in the following screenshot:
Here we choose 1 to select English, and press ↵ Enter.
Now airgeddon is ready to run the attack. All parameters and requirements are set. The attack is going to start. Multiple windows will be opened, don’t close anyone. When we want to stop the attack press ↵ Enter on this window and the script will automatically close them all.
We can see lots of terminals here for various works like de-authentication, control, DNS, Web Server etc.
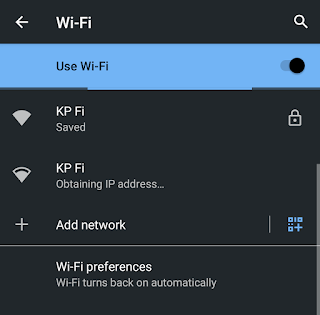
Now we can see on our mobile device that we are not connected to our locked main WiFi access point and there are another access point with same name, in the following screenshot:
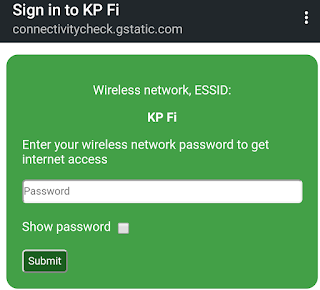
Whenever we connect to the other network. It automatically redirect to log in, as shown in the following screenshot:
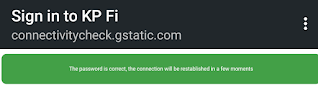
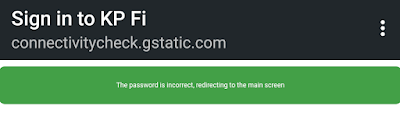
Now here if our target use the password it will show the user that it was correct password.
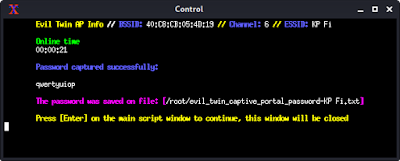
We get it on our txt file on root directory. It also shown in the control terminal window. We need to keep the terminal windows open until the user did not put his password on the login screen. Hope target is not sleeping.
Here in this evil twin attack we are using the handshake file to check the password is correct or not. If they put the wrong password then it will notice it. Isn’t is amazing?
There are many types of attacks we can perform using airgeddon against a wireless network. Here we discuss about only two type because everything is very easy here. We just need to select the options only, everything will be done by the script automatically.
This is how we can install and use Airgeddon on Kali Linux. This is a very easy but powerful tool for WiFi auditing.
Airgeddon is specially designed for Linux. Airgeddon did not compatible on MacOS/OSX, because Aircrack suite does not support airodump and aireplay for OSX/MacOS, and iwconfig does not exist in OSX/MacOS.
Airgeddon is not working with any Linux distribution run under Windows subsystem (WSL). Airgeddon also didn’t support native OpenBSD and FreeBSD, iwconfig command not working there and ifconfig shows different output.
Warning:- Attacking other’s network or WiFi is not legal. We publish this article for educational purpose and tested things on our own devices. If anyone attacks on others devices then we and the tool creator will not be responsible for that.
Stay updated with our articles by following us on Twitter and GitHub. Be a part of the KaliLinuxIn community by joining our Telegram Group, where we focus on Linux and Cybersecurity. We’re always available to help in the comment section and read every comment, ensuring a prompt reply