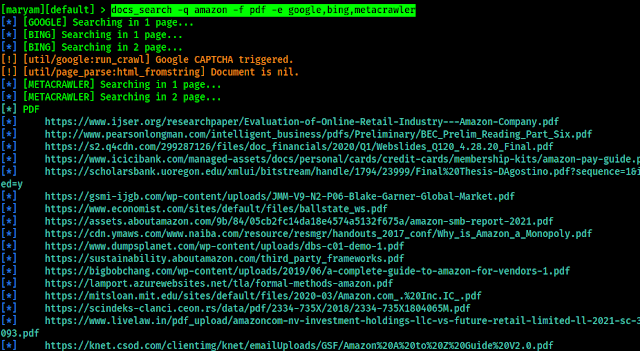
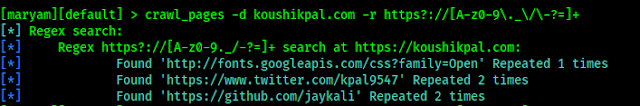
How Progressive Slots Look Like In The Future
What are Progressive Slots, and How Do They Work?
Progressive jackpot slots have been around for a long time and are great to play, just like ordinary in-game jackpot slots. With progressive slots, the total jackpot amounts constantly change because a small amount of your wager is added every time you bet. This applies to every slot player on the network, so they end up with astronomical jackpot amounts with progressive slots.
The appeal of progressive slots is the potential to win a massive sum of money with only a small wager. The tricky part is that the winner is based on a random number generator (RNG), so it’s hard to predict who will win or when the next win will happen (though many have tried). The reverse could also occur where someone wins while you are playing, and that depletes the pot drastically, meaning if you were to win next, the jackpot might be significantly less.
 |
| Image by LoggaWiggler from Pixabay |
Tips For Playing Progressive Slots
There is no formula to win at Progressive. It is 99% based on luck, but we will share some tips that may help you.
- Choose a reputable casino to avoid winning and not getting your winnings.
- Manage your budget, as tempting as it may be, to keep playing, thinking the next spin may be it, reign in your spending, and bet only money you can lose.
- Go for the maximum wager (within your budget, of course).
- If you ever win the jackpot, don’t spend it all; engage a financial advisor.
The Future of Progressive Slots
Innovation and technological advancements have made an impact in every industry, and that includes the gambling industry. So where do we see progressive slots in the future? Without a doubt, they will still be around ten years from now. But we must admit that they are declining in popularity, and more than the big jackpot wins are needed to draw new players in.
“Poker-Faced” New Age Players
Players have more information on how progressive slots work and the odds of winning. Some say as high as 50,000,000 to 1; this has put off many players who would rather play something with better chances. Players also understand how RT works, and its meaning; progressive slots tend to have a lower RTP than most slot games. Many gamblers prefer table games where you can win based on strategy and skill. That’s why there has been an increase in popularity around card games like Blackjack and Poker; once you have mastered the poker terms and slang and have a solid strategy, you can see some returns.
With Gen Z coming of age and partaking in gambling, there is a shift to more technologically advanced games and a more interactive and social player experience. Slots, in general, could be more interactive games and can be pretty lonely. Ultimately, table games offer better value for players in monetary returns and social interaction. Even when playing online, you can interact with the dealer, and depending on the casino, you can interact with other players.
Accumulative Cost
Another downside with progressive jackpots is you need to know when or how much you will win; you could be playing consistently over a couple of months only to have someone win the jackpot just after you log off. And unlike lottery tickets or games like craps and roulette, it could be weeks, months, or years before the jackpot is won. That is a lot of money used to wager over time.
Simplicity
Progressive slots are easy to play, and the rules are just as easy to understand, and this is a drawcard for many people. Many games also have a lower-tier jackpot which is also progressive, but players have a higher chance of winning; this is another reason players keep playing. The minimum wager amount is a drawcard for players vs. other casino games. So with as little as $0.50, you can win millions without effort by pressing the spin button.
The Jackpot Amounts
No matter how indifferent you are to progressive jackpots, the thought of walking away with $20 million has crossed your mind. These are the amounts many have walked away with in progressive jackpot winnings. Mega Moolah, nicknamed “Million Maker,” has had the most lucrative wins. In January 2019, a massive $20,057,034, while the following year, a $13,615,861 jackpot was won through Luxury Casino. The thought of those millions coming our way does keep us playing these slots.
 |
| Image by jacqueline macou from Pixabay |
Last Word
In most online casinos, over 50% of their game library is dedicated to slot games, and progressive slots form part of that. With the integration of virtual reality and mixed reality in the gambling space, we can only hope it will improve how we play slots and we can enjoy the experience even more. We don’t foresee a gambling experience without progressive slots, no matter how unpopular they may get amongst experienced players. And frankly, it would be boring without them around to remind us of what we could win.







































.webp)