How To Secure Our Kali Linux System To Ensure Our Protection
Kali Linux is an open-source Debian based Linux distribution which mostly used for offensive security. Previously known as Backtrack Linux this Linux distribution is a symbol of security itself. Kali Linux used by penetration testers around the world. It also used by cybersecurity students to practicing penetration testing and stuff. But to run Kali Linux with the default settings may be a bad idea.
Why? Because default settings are easy to crack and Kali Linux is not a privacy focused distribution (like Tails OS), Kali is created for attacking not for defending. Security is a huge concept. Most people use Kali to test security, but it’s also very important to secure the Kali itself. Because it is based on Debian we got good security. But what if we need more security?
In this article we are going to discuss how we can improve the security of our Kali Linux system. Running Kali Linux with the default settings is not be a good idea.
Change the Default Password
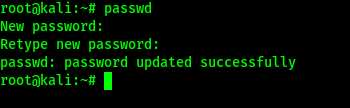
If we are using older Kali Linux versions (older then 2020.1) then our default credential is “root” “toor“. If we have newer Kali Linux versions then the default credential is “Kali” “Kali“. We need to change it ASAP. It’s easy. We need to run following command on our Kali Linux terminal:
This simple command will ask us the current user’s password (default if we don’t change it already). Then it will prompt for a new password and again it will verify it. A good password should contain both uppercase and lowercase letters with scrambles of symbols and numbers. After verifying the password our password will be changed. We can see it on the following screenshot:
We need to remember that our typed password will not displayed for security reasons.
Unprivileged User Account
Previously root user was Kali’s default user. Now things are changed after Kali Linux 2020.1 update. Now Kali’s default user is non-root user account.
An unprivileged user stands directly below the main admin user which have all the root permissions. Similarly to family and parental accounts.
We can even use a root user directly on our system, but it will not good for security reasons. We must not use root user always.
Updating Kali Linux Frequently
There are lots of versions of Kali Linux. Kali Developers releases a new version in every quarter. Updated versions of Kali comes with upgraded kernels. For being a rolling distro Kali Linux doesn’t need to be download ISO image and again install it during update. We just need to apply some commands to install the update. Follow us to get notified when the update comes.
Also we must update and upgrade our Kali Linux after some days by using following command:
The conclusion is we need to update & upgrade Kali Linux frequently and update the distribution whenever it release.
Changing the Default SSH Keys
Secure Shell or SSH is a network protocol. It uses to communicate computers securely. As we’re on this page via web, we are already using some kind of SSH. There are no way around it but to fix present or upcoming security issues. Even for distros we use, there are SSH keys that let us verify authentic files from a source.
It may looks everything is fine and cool but the problem is for everyone there are the same keys. Let’s understand it on this way. If we download a software from a website, it is the same distribution copy that everyone downloads it. Later we use our accounts with the software for a personalized way, and the service provider gives adequate power according to the subscription under those accounts. SSH keys have quite same fundamentals but those are used to verify files.
If a bad guy did a Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack or a social engineering campaign it may drain our security.
SSH gives us capability to authenticate without inputting passwords every single time. There are two types of SSH keys. One is public and the other one is private. We need to change the our public SSH keys, because every distro have the same, and generate a private key will make sure only authenticated users can access it.
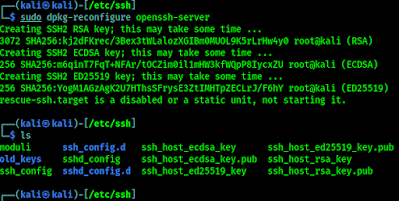
SSH keys are located in /etc/ssh directory by default. This list view will shows all the keys inside. Instead of deleting them from the database, we are going to store them some secure place. We use following commands to do this:
Now our all old SSH keys moved to a directory named old_keys.
Now we generate new keys by using following command:
This command will generate new SSH keys for us. As we can see in the following screenshot.
If we faced any problem then we can use our backed up SSH keys.
Save our Identity
During surfing the internet with a Kali Linux machine, we can use the “NIPE” or “kalitorify” tools to browse safely and anonymously. Even though “macchanger” is recommended to spoof our Mac address. We also advice to change our hostname from Kali to a nameserver, and add a host similar to 8.8.8.8.
Monitoring Logs
Analyzing the logcheck program can be a real life saver. It can send logged messages directly to admin’s email. Log files are locally stored inside “/var/log” by default.
Using top (built right into the system) or htop (sudo apt install htop) tool shows us real-time monitoring activity. Even the xfce4-taskmanager graphical tool can perform similar actions.
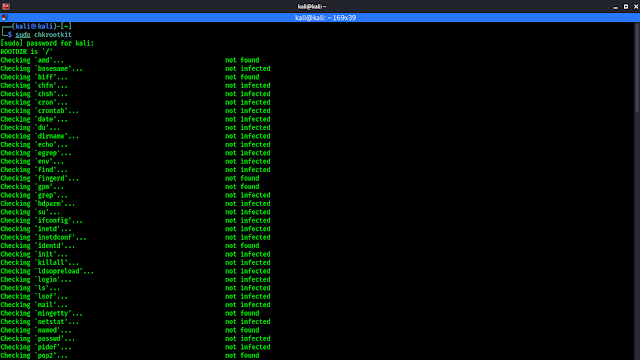
Scanning for Malware and Rootkits
We also need to scan our system frequently for malwares and rootkits. We can run the scan by using “Chkrootkit” or “Rkhunter” tool kits. We have discussed about this topic some days ago in details (Find & remove rootkits from Linux). So we don’t think we have to repeat it. These tools are like anti-malwares for Linux systems.
Extra Talks
Although Kali Linux is created for attacking purpose it is quite secure environment itself. But advanced users goes above and beyond for daily tasks and it is necessary to follow proper procedures. New users coming from other operating systems like Windows may think just running Kali Linux inside VMWare or VirtualBox is the safest process. It is quite true but certain steps must be taken.
Hope this article helps our fellow Kali Linux users. Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.