Masscan is the fastest network port scanner. It can scan the whole internet under 6 minutes with 25 millions per second data transmitting speed. Is it faster than flash?
This fastest port scanner gives the output like nmap but masscan works like unicornscann, Zenmap internally(asynchronous scan). It is faster because of flexibility allowing arbitrary ranges and port ranges.
Masscan uses it’s own custom TCP/IP stack. Anything other than a simple port scan may cause conflict with the local TCP/IP stack.
We will discuss later the differences between masscan and nmap, now let’s check how to install and use masscan in our system.
Installing Masscan
Masscan comes pre-installed with the Kali Linux full version. We can check the basic uses by simply enter following command:
masscan
If our system doesn’t have masscan then we need to install it. Before installing it we need to install it’s dependencies by using following command:
sudo apt-get install clang git gcc make libpcap-dev
Then we can install it by applying following command:
sudo apt-get install masscan
Dependencies doesn’t require to install it, these dependencies help masscan to work perfectly. We also can install it from it’s GitHub repository. The following commands will be useful to install it from Git repository.
git clone https://github.com/robertdavidgraham/masscan
cd masscan
sudo make
Uses of Masscan
Masscan is used for scan a network, if we want to scan a single port then we can perform it by applying following command:
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p443
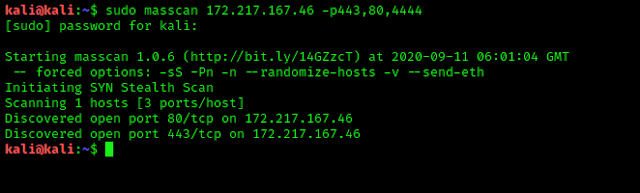
This will scan for a single port 443.
We also can use this tool to scan multiple ports separated by comma(,). The example is following:
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p443,80,4444
To scan a range of ports we can use following command:
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p12-443
The above command will scan for port 12 to port 443 on our given IP address.
So in case we need to find all the ports then we can use following command;
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p0-65535
There are a limited number of ports, that is 65535. The above command will check for every port.
Lightning Speed!
We said that masscan is the fastest scanner but after using previous commands we didn’t feel that it is faster.
The reason is masscan scans at the rate of 100 packets/sec, which is slow. To increase it we need to use –rate flag with it.
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p0-65535 --rate 25000000
Using the above command we can achieve the fastest speed (25 million packets/sec).
One more thing, we can’t achieve the max speed on Mac, Windows or Virtual Linux systems. Masscan works best on primary installed Linux systems. On other systems we can get only 300,000 packets/sec. That is really fast but with the Linux system we can get the maximum speed.
To scan faster we must need to have a very good internet connection. Usually it happens that masscan can achieve the highest speed but our internet connection can’t send 25 million packets per second. Although the speed we got was faster than any other port scanner.
To see the fastest effect we should choose a bigger network to scan. On small networks or in single IP we can’t see the faster speed in our eyes. Because scanning small networks is work of some seconds so we can’t feel the speed. Let’s talk about it.
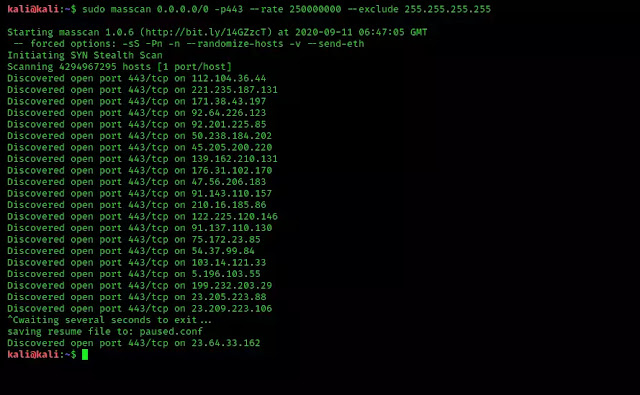
Masscan can scan the entire internet in 6 minutes according to it’s author Robert Graham. If we want to scan the whole internet for a specific port (443 port for example) we can use following command:
sudo masscan 0.0.0.0/0 -p443 --rate 250000000 --exclude 255.255.255.255
This command will scan the whole internet for 443 ports, and show us the result as fast as possible. Here we have stopped the scanning. We can see the screenshot.
This is how we can find a specific or vulnerable port all over the internet.
Some More Uses
To save the output result in a file we can use following command:
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 -p0-65535 > example.txt
Not only txt format we also can save the results in XML (-oX), Grepable (-oG) and JSON (-oJ) formats. We like the Grepable format because we can use the output on other tools.
We also can scan a network for the top ports. So if we give it ‐‐top-ports 100. It’ll scan the top 100 most common ports discovered according to nmap. We can choose our top ports numbers, an example of this is following (Scans for top 10 ports):
sudo masscan 172.217.167.46 --top-ports 100 --rate 100000
There is a pause function in masscan, Yes we can pause the scanning process and resume it when we need. Scanning on a large network we found it useful. During the scanning process we can press CTRL+C then after some seconds it will pause it and save a paused.conf file. This file has all the settings and progresses from the scan. We can resume the scanning process again by using following command:
sudo masscan --resume paused.conf
Nmap vs Masscan
In this article we have learned that masscan has very good features, the output looks like nmap but there are lot’s of differences between. Those are following:
- Nmap uses synchronous mode scanning which is very slow but accurate but masscan uses asynchronous mode scan which is very fast but not so much accurate.
- Masscan doesn’t check if the host is up or not, it always treats the host as online but nmap always checks if the host is up or down.
- Masscan never converts domain names to IP addresses. We manually need to find the IP address and provide it to masscan. But nmap works finely with IP and domain names.
- We always need to specify ports on masscan.
To know more about nmap vs masscan we can check this article.
There are also some similarities in nmap and masscan. Masscan have some nmap compatible settings/ flags. To check them we can use masscan -nmap command.
Masscan Web UI
The Offensive Security team has created a web interface for masscan. Using that process we can use masscan on a easy web based GUI. Here is the full guide from Offensive security.
That’s all about masscan. Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxInfamily, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.