Kali Linux 2021.3 Update is Here !
The third update of Kali Linux in 2021 is live and ready to ROCK.
Say Welcome to Kali Linux 2021.3! This release welcomes a mixture of new items as well as enhancements of existing features, and is ready to be downloaded (from our updated page) or upgraded if you have an existing Kali Linux installation.
A quick summary of the change log since the 2021.1 release from February 2021 is:
- OpenSSL – Wide compatibility by default – Keep reading for what that means.
- New Kali-Tools site – Following the footsteps of Kali-Docs, Kali-Tools has had a complete refresh.
- Better VM support in the Live image session – Copy & paste and drag & drop from your machine into a Kali VM by default.
- New tools – From adversary emulation, to subdomain takeover to Wi-Fi attacks.
- Kali NetHunter smartwatch – first of its kind, for TicHunter Pro
- KDE 5.21 – Plasma desktop received a version bump.
OpenSSL: wide compatibility by default
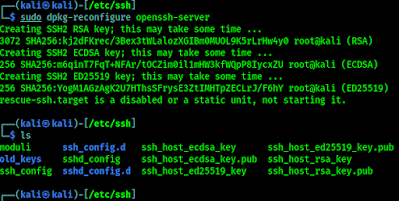
Going forwards from Kali Linux 2021.3, OpenSSL has now been configured for wider compatibility to allow Kali to talk to as many services as possible. This means that legacy protocols (such as TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1) and older ciphers are enabled by default. This is done to help increase Kali’s ability to talk to older, obsolete systems and servers that are still using these older protocols. This may potentially increase your options on available attack surfaces (if your target has these End of Life (EoL) services running, having then forgotten about them, what else could this uncover?). While this is not a configuration that would be good for a general purpose operating systems, this setting makes sense for Kali as it enables the user to engage and talk with more potential targets.
This setting is easy to modify via the command-line tool kali-tweaks though. Enter the Hardening section, and from there you can configure OpenSSL for Strong Security mode instead, which uses today’s current modern standard allowing for secure communication.
For more details, refer to the documentation: kali.org/docs/general-use/openssl-configuration
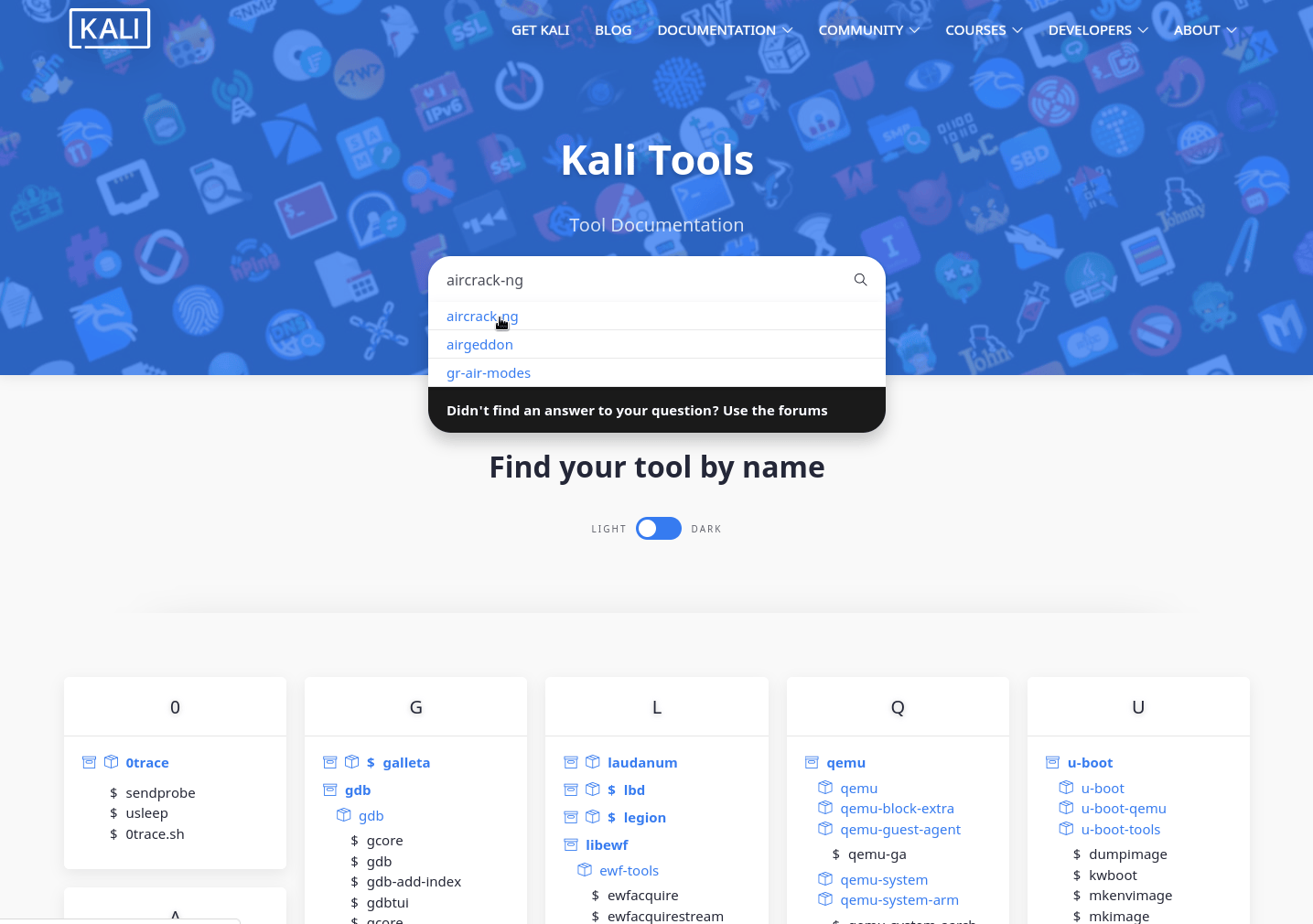
Kali-Tools
In 2019.4 we moved our documentation over to our updated /docs/ page. It’s now finally the turn of our Kali-Tools site!
We have refreshed every aspect of the previous site, giving a new, faster, layout, content, and system! The backend is now in a semi-automated state and more in the open, which like before, allows for anyone to help out and contribute.
Once these sites have settled down from all the changes and matured a bit, we will start to package these both up, allowing for offline reading.
Virtualization: improvements all over the place
The Kali Live image received some love during this release cycle! We worked hard to make the experience smoother for those who run the Live image in virtualized environments. Basic features like copy’n’paste and drag’n’drop between the host and the guest should now work out of the box. And this is really for everyone: VMware, VirtualBox, Hyper-V and QEMU+Spice. Did we forget anyone? Drop us a word on the Kali bug tracker!
On the same line: it’s now very easy to configure Kali for Hyper-V Enhanced Session Mode. Open kali-tweaks in a terminal, select Virtualization, and if Kali is running under Hyper-V, you’ll see a setting to turn on Hyper-V Enhanced Session Mode. It’s now as simple as hitting Enter!
If you use this feature, make sure to visit kali.org/docs/virtualization/install-hyper-v-guest-enhanced-session-mode/, as there are a few additional things to be aware of.
Many thanks to @Shane Bennett, who spent a tremendous amount of time testing this feature, provided extremely detailed feedback all along, and even helped us with the documentation. Kudos Shane!
New Tools in Kali Linux 2021.3
It wouldn’t be a Kali release if there weren’t any new tools added! A quick run down of what’s been added (to the network repositories):
- Berate_ap – Orchestrating MANA rogue Wi-Fi Access Points
- CALDERA – Scalable automated adversary emulation platform
- EAPHammer – Targeted evil twin attacks against WPA2-Enterprise Wi-Fi networks
- HostHunter – Recon tool for discovering hostnames using OSINT techniques
- RouterKeygenPC – Generate default WPA/WEP Wi-Fi keys
- Subjack – Subdomain takeover
- WPA_Sycophant – Evil client portion of EAP relay attack
Kali Nethunter Updates
We proudly introduce the world’s first Kali NetHunter smartwatch, the TicHunter Pro thanks to the outstanding work of our very own NetHunter developer @yesimxev. It is still experimental, hence the features are limited to USB attacks, and some basic functions. The hardware also has limitations, as such a small battery won’t supply enough voltage for any OTG adapters, so huge antennas won’t stick out of your wrist! The future is very promising, bringing support for Nexmon and internal bluetooth usage.
The image is available on our download page.
Please note that those images contain a “nano Kali rootfs” due to technical reasons. The detailed installation guide can be found in our Kali documentation. Feel free to join the adventure!
Kali NetHunter Installation via Magisk
Thanks to the amazing work of @Mominul Islam, we can now bring Kali NetHunter to Android 11 devices without a fully working TWRP!
Each Kali NetHunter image can be flashed as a Magisk module. This work is still in its infancy and more work is needed to bring it up to par with the traditional installer through TWRP.
One of the missing parts is the kernel installation. We haven’t been able to install the kernel through Magisk yet. That has to be done via kernel installers like the “Franco Kernel Manager”. If you are keen to get NetHunter onto your Android 11 device, just give it a crack. If you are interested in helping out with getting the kernel part finished, please get in touch with us through our GitLab issue tracker. Any help is greatly appreciated!
Kali NetHunter installation step-by-step guide for our preferred device, the OnePlus 7
Our preferred device for Kali NetHunter is the OnePlus 7 running Android 10 (stock ROM).
For a step-by-step installation guide and links to all the files required to restore your phone to the latest stock Android 10 ROM, install TWRP, Magisk and Kali NetHunter, head over to our Kali documentation page.
Kali ARM Updates
We have been busy doing various tweaks and tinkering on our Kali ARM images, which covers:
- Our Kali ARM build-scripts have been re-worked.
- Thanks to @cyrus104, we now have a build-script to support the Gateworks Newport board, and he also added documentation for it.
- @Re4son contributed a build-script for the Raspberry Pi Zero W based “Pi-Tail” (Find more information here).
- Additionally, the RaspberryPi Zero W based “P4wnP1” build-script has undergone some major changes.
- All images should finally resize the file-system on the first boot.
- We now re-generate the default snakeoil cert, which fixes a couple of tools that were failing to run previously.
- Images default to
iptables-legacyandip6tables-legacyfor iptables support. - We now set a default locale of
en_US.UTF-8on all images, you can, of course, change this to your preferred locale. - The Kali user on ARM images is now in all of the same groups as base images by default, and uses zsh for the default shell. You can change your default shell by using the
kali-tweakstool which also comes pre-installed. - Raspberry Pi images can now use a
wpa_supplicant.conffile on the/bootpartition. - Raspberry Pi images now come with
kalipi-config, andkalipi-tft-configpre-installed. - Pinebook Pro’s kernel has been updated to 5.14, and you now get messages on the LCD screen as it’s booting, instead of a blinking cursor until X starts.
Desktop & Theme Updates
There are also some changes in the desktop space:
- Improved GTK3 theme for Xfce’s notifications and logout-dialog
- Redesigned GTK2 theme for a better fit of older programs
- Improved Kali-Dark and Kali-Light syntax-highlighting themes for GNOME and Xfce
In addition to these changes, one of Kali’s preferred desktops, KDE plasma, has received a version bump, now including version 5.21. This update brings an updated look, with a new application launcher and theme improvements. Here’s a preview of how it looks with Kali’s customization:
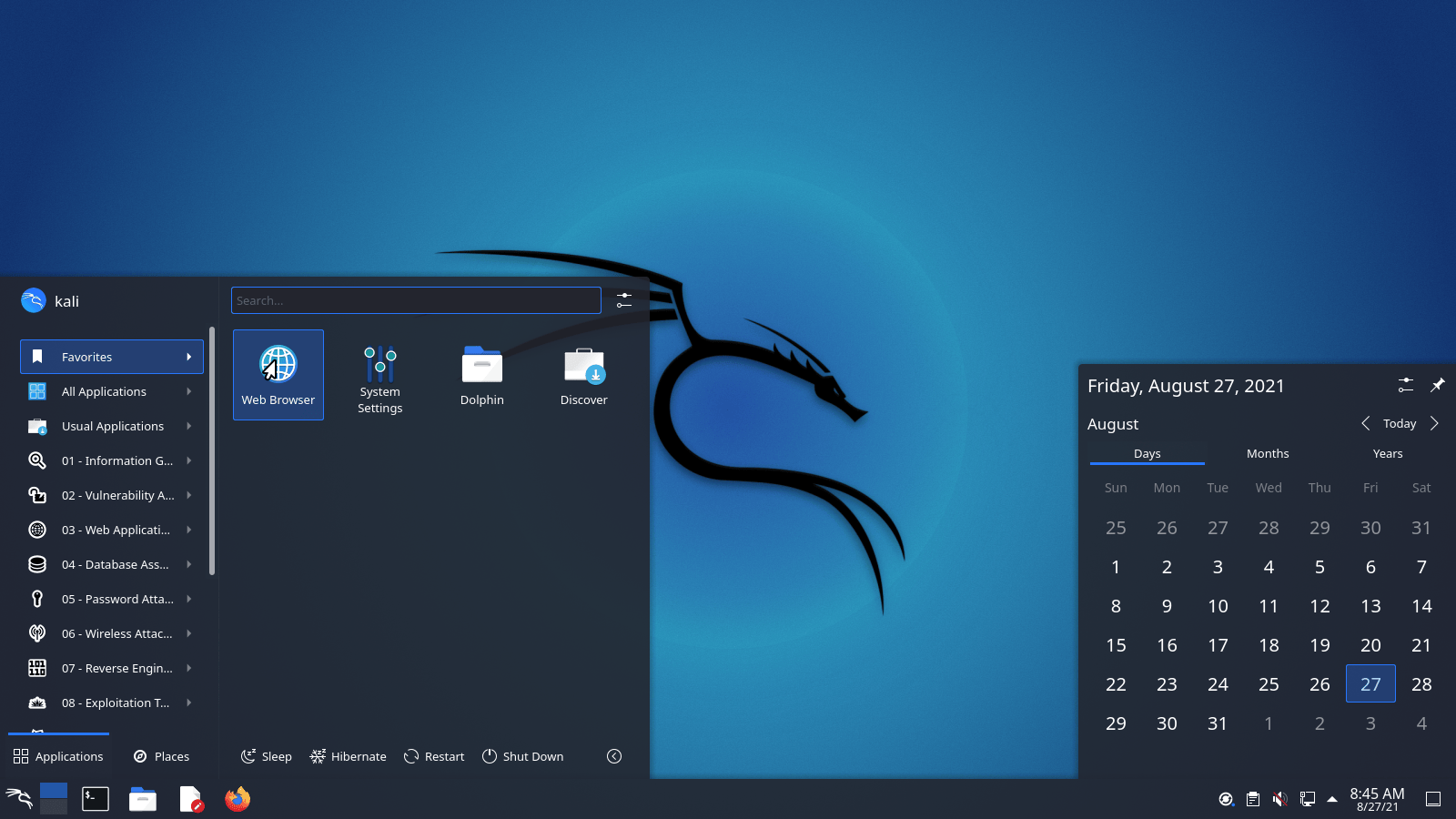
Kali Docs Update
Our documentation site, as well as the pages mentioned already in this blog post, the following other pages have received major changes:
- Download Kali Linux Images Securely
- Kali Linux & WSL & Mesa
- Kali Linux IRC Channel
- Contributing runtime tests
GitLab Commit 2021
We participated in GitLab’s virtual conference this year and @g0tmi1k gave a talk on the Dynamic between Kali Linux and OffSec. Give it a watch!
Ampere and ARM
Following our announcement of our partnerships with Ampere, we have now fully moved our ARM package building machines over to their hardware, and loving the speed increase! Thank you again to Ampere for the assistance! If you need some ARM servers give them a look! If they are nice enough to help us out this way, we are sure they will treat you good as well.
Upcoming Changes
Looking forward, we are going to be announcing the following changes:
- Kali-Menu refresh – We know you may not use it, but for the people who do, we are planning on making some major alterations in its structure. This will hopefully be live for testing in 2021.4, and then made default in a later release based on user response. You will be able to change the menu layout by using
kali-tweaks. If you want to provide input on this change, get engaged with us and make your voice heard! - Load Balancer (http.kali.org & cdimage.kali.org) – This handles apt packages as well as OS images. We will be switching from MirrorBrain to MirrorBits. We will be soon in touch with all the community mirror maintainers to give them notice of our infrastructure changes. If you would like to become a mirror, please see our guide.
Download Kali Linux 2021.3
Fresh Images: So what are you waiting for? Start downloading already!
Seasoned Kali Linux users are already aware of this, but for the those who are not, we do also produce weekly builds that you can use as well. If you cannot wait for our next release and you want the latest packages (or bug fixes) when you download the image, you can just use the weekly image instead. This way you’ll have fewer updates to do. Just know that these are automated builds that we do not QA like we do our standard release images. But we gladly take bug reports about those images because we want any issues to be fixed before our next release!
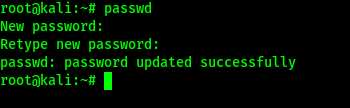
Existing Installs: If you already have an existing Kali Linux installation, remember you can always do a quick update:
You should now be on Kali Linux 2021.3. We can do a quick check by doing:
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ grep VERSION /etc/os-release
VERSION="2021.3"
VERSION_ID="2021.3"
VERSION_CODENAME="kali-rolling"
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ uname -v
#1 SMP Debian 5.10.46-4kali1 (2021-08-09)
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ uname -r
5.10.0-kali9-amd64
NOTE: The output of uname -r may be different depending on the system architecture.
As always, should you come across any bugs in Kali, please submit a report on our bug tracker. We’ll never be able to fix what we do not know is broken! And Twitter is not a Bug Tracker!





![How to Stay Anonymous Completely [100% Perfect] How to Stay Anonymous Completely [100% Perfect]](https://infocerts.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/How-to-Stay-Anonymous-Completely-100-Perfect-infocerts.jpg)