Scalability
Incompatibility issue (SC1)
Information from articles that discuss about portability, interoperability, scaling quickly, smart scaling, automatic scalability, security management function, collaboration, Integrity of security, general requirement cloud security management model are considered. For instance there might be a situation arising where a user wishes to change his Cloud Service Provider (CSP), in such situation the new CSP should be capable in moving data from an old service provider. This transfer includes data, components and also security policies. In most cases user won’t be provisioned to take physical firewall but users should make sure to have a copy of its configuration on virtual machines [3]. There are chances of customer goes locked to a SP if the customer chooses a wrong service provider [109][105]. Cross data center operations would find this as a serious issue [55]. In article [91] author mentions that controlling defining and ordering in relation to security are one of the ten things to be noted while shifting to cloud computing.
CSPs are creating the Hosting world using “sticky services”, these services are reasons for causing difficulty in moving between different service providers. Example, the Amazon’s simple storage service S3 is incompatible with IBM’s blue cloud or Google or dell [24][130][46]. Open cloud manifesto which was newly
published was declined by both Microsoft and Amazon and are pursuing interoperability on their own terms [46][16][24][173].
Things to be noted before/after moving from one CSP to another are [3]:
• In infrastructural service, backing up of data is easy compared to other services.
• In case of Web application, there should be a perfect plan and process on how and when to move data. If all of your data is visible then it is not necessary to move it completely, but instead necessary data can be selected and copied.
• Application migration and reconsidering application infrastructure are areas to be considered by infrastructure architects. This is because some companies such as Microsoft are provider-specific and are not built to be easily reused
When data is stored in the cloud, there are some virtual perimeters and security models with some shared responsibilities, among CSP and customer. These shared responsibility models will induce some changes into organizations IT staff. To maintain stability in the organization, the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is required to know if the cloud service provider allows its user to control and manage implementation of security policies and get assurance that business data in cloud stays protected. To assure data stays protected there are two considerations, one is that there should be an analysis made to find out what additional security controls need to be implemented on existing controls provided by CSP. The other point to be noted is how enterprise Security management tools and process adaptation manage security in cloud [104]. Policy integration task in the cloud should also be able to address secure interoperability, semantic heterogeneity and policy evolution management [148]. Scalability of storage: One advantage with cloud computing is that it can
provide infinite capacity based on demand of the user. Its not yet clear on how persistent storage systems could be when it is practically implemented. The attempts to provide these scalable conditions was done by trying to vary richness of query and storage API’s. There is still a challenge in this area for the researchers i.e., not only to meet the expectations of programmers in providing durability, high availability and ability to manage data quickly but also to combine these qualities with cloud where advantages of scaling up and down can be used efficiently [13][12].
Interoperability: Interoperability is an important to maintain global stabilization to reduce rework and management [41]. Organizations willing to adopt cloud computing wish to have an Identity Management (IdM) solutions that can interoperate with all the existing IT systems and solutions, with or without small changes. Some of the most commonly used authentication mechanisms are Microsoft Windows authentication, SSO, LDAP, SAML, OPENID and OAUTH, OpenSocial, FaceBookConnect, etc., and cloud users expect easy integration with these types of services. To conclude CSP would have to provide an authentication module where each and every type of authentication system that user wishes, to use are easily comparable with cloud system [61]. Organizations are interested in CSP’s, who provide a framework which can enable interoperability with different other Service Providers (SP), Amazon API’s standards, are the most commonly used standards to design other on demand instances. CSP’s which use these API standards are easily comparable with Amazon (Amazon EC2 can run easily in Eucalyptus). In certain situations cloud service providers which assure to provide interoperability with other SP is also problematic, example Hadoop which provides on demand capacity can’t for sure provide compatibility to run on another system developed using C++. Several organizations such as Cloud Computing Interoperability Forum and Open Cloud Consortium are still trying to provide firm and stable standards for CC. There is a framework named as ‘Thrift’ which relies on code-generation engine, to provide scalable cross-language services development. To provide interoperability and compatibility with various programs there could be a common language, which can be used by different service providers. As a solution to this several people attempted but there is no single language that is up to the requirement [63]. A panel report on cloud computing standards discussed about proposing “open standards and Predictive Markup Language (PMML)” and expressed views that implementing these could be extremely helpful not only for software vendors and data mining community in general
Constant feature addition (SC2)
In cloud computing scenario users need to be updated with new security features. These updates need to be done by the service provider and are required to be quick. The rate at which updates are installed can effect security as well as Software development lifecycle
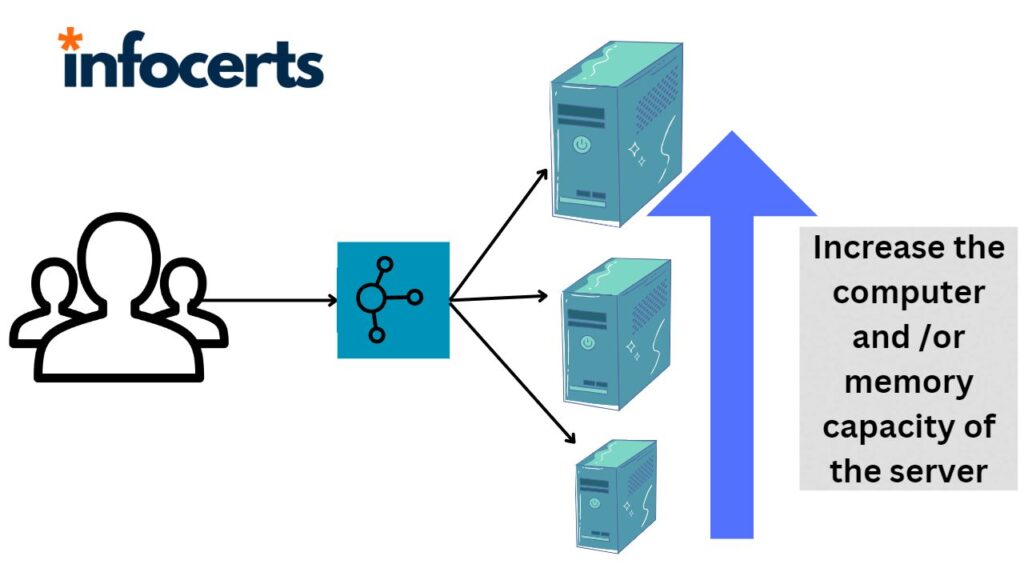
Scalability (SC3)
CC requires the ability to scale multiple transactions managed over multiple connections. Scaling the resources manually is still persistent with IaaS, where SP will define how the service has to be scaled based on personal experience and different factors influencing it [109]. There should be a reduction in management
tasks and automatic scaling with-in the CC applications should be enhanced [131]. With software today it takes approximately 6 months for a single SAML/SSO connection, which does not address the compliance and access control issues [151]. Open cloud manifesto states that, to keep out of problems with allocation of resources during peak hours cloud services have to dynamically scale up and down
——————————————————————————————————————–
Infocerts, 5B 306 Riverside Greens, Panvel, Raigad 410206 Maharashtra, India
Contact us – https://www.infocerts.com