This article says about Confidentiality and Privacy, one type of category comes under Challenges in Cloud Computing.
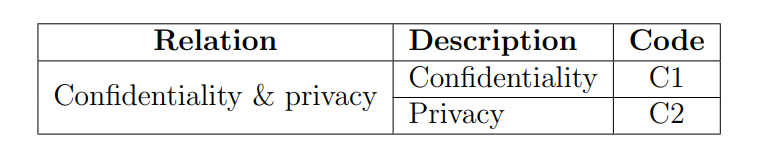
Confidentially (C1)
Confidentiality plays a major role in securing organizational content stored across different databases [65]. It’s a key issue and since most data is virtually accessed, protecting and maintaining confidentiality of user profiles is of utmost consideration [123][136][177]. Viruses, trojans, malwares, etc., are some unauthorized ways to exploit customer’s information [67]. In some cases it is also important for an organization to handle data remains, this is to protect the confidentiality of an employees information even after his data is removed or erased. Remanence is an issue that can lead to the disclosure of private data [179]. In article [48] author mentions that even though there are methods to provide Confidentiality they are not widely used by SPs. As a special case in [142] author mentions that because of confidentiality agreements made with user, preventing/identifying malicious attacks is becoming difficult (top threat mentioned by CSA). This is because a SP can not monitor or look what’s happening in the user’s space due to confidentiality agreements, which can be exploited by malicious users for unauthorized activity [142][90].
To prevent data being disclosed or misused in cloud and protect customer’s data, every customer should be educated as to how data is stored in the cloud. By doing this the user will be careful while storing sensitive data in the cloud
Privacy (C2)
Privacy is one of the Cloud Computing security requirement [92][65][74][109][160][54][126].
Keeping data private in a distributed system is challenging when compared to personal possession and in CC it is risky [149][23]. Privacy or obligation is related to the collection, use, storage, disclosure and destruction of data that is personal to someone. The rules and the concept of privacy varies with countries, cultures and jurisdictions [104][111][74]. The author in [179] mentions privacy as a desire to control disclosure to his personal information and presents that there are a number of legal challenges to cloud. Privacy is being accountable to an organization’s data subjects and also be transparent towards organizations practice around personal information, there is also a little knowledge on how privacy laws that govern within an organization [111]. There is no universal agreement towards defining what constitutes personal data. “The rights and obligations of individuals and organizations with respect to the collection, use, retention, and disclosure of personal information.”, is one way of defining privacy and this is gaining popularity among American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and the Canadian Institute Of Chartered Accountants (CICA) in the Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP) [104]. As a special case in [142] author mentions that because of privacy agreements made by the user, preventing/identifying malicious attacks is becoming difficult (top threat mentioned by CSA). This is because a SP can not monitor or look whats happening in the user’s space due to privacy agreements, which can be exploited by malicious user for unauthorized activity [142][90]. And this case preserving privacy i.e., protecting the Private Data from unauthorized users in cloud computing while maintaining sharing of resources is a security issue [177][17][140][75].
Services can keep varying among customers and also the service providers in CC, since these services keep changing private data and personal data moves within an organization or could also cross organizational boundaries and protecting such information is important. Fields such as financial and health, are concerned about safety of data. Following are most important privacy risks, which need to be covered [117]:
• In case of a user, he might be forced or persuaded to give his personal information against his will [49].
• From organizations perspective, compliance with origination policies, legislation, creditability and loss of reputation are some other issue.
• With implementers of cloud platform, possibility of exposure of sensitive information that will be stored on platform, Legal Liability, loss of reputation
and credibility, lack of user trust and take-up.
• For providers of applications designed over the cloud platforms, loss of reputation, legal noncompliance ‘function creep’ which uses the personal information stored on the cloud (i.e., it might later use for purpose other than that for which it was originally intended).
• In case of Data Privacy, exposure of personal information. To prevent loss of personal information there is a need for a special committee, which keeps track and makes decisions related to data privacy. If a security compliance team already exists within an organization it won’t be having formalized training on data privacy, a possible solution to this is to hire a privacy expert or train an already existing member well [119].
• Organizations can be held liable even if the subcontractor causes security breaches and CSP is legally considered same as that of a subcontractor.
This confirms that organizations should ensure that a CSP is/are compliant to respective privacy legislations. Various governments have posed laws,
which make them accessible to data stored in their jurisdiction for electronic discovery or anti-terrorism purposes. To gain access to data stored in the cloud i.e., search for data in cloud government should in most cases issue a search warrant and this can differ from service provider to a service provider. In some cases CSP fails to provide required computing resources, in such situations CSP may be forced to outsource data for a different CSP. The subcontracting CSP’s don’t inquire about compliance with privacy regulations when establishing a relationship. The organizations are not aware of these privacy regulations or they think these are not important to comply with. Raising Awareness about both issues and existing regulations seems like a good step to solve this issue [132].
The author of [166] suggests that privacy of user data and laws regulation and policies need to be framed taking CC into context, which will prevent security and user involvement in using the CC application. Methods like homomorphic encryption technique, which helps to protect data will complicate handling huge amounts of data and in an environment where data keeps growing is tough [23].
Providing individual user control, anonymous services for individual use, limiting identity information, and requiring authentication for high level transactions are some of the features that safeguard privacy of users. For this SPs have to encrypt the user information, isolated data processing and storage, managing privacy and security requirements are some of the issues to be dealt while working in cloud computing [122]. Also transaction histories, identity information, Policy Components during integration, etc., need to be included and protected
privacy