We all know that cracking passwords are very important in cybersecurity field. Then ever we thinks for password cracking we either need to do dictionary attack or brute-force. But, if the password didn’t in our password list dictionary attack will not work and brute-force takes too much time to crack a password (sometimes even more than a decade).
Trying to solve this problem of brute-force password generator a tool is there by the makers of HashCat (well known password cracking tool). This tool named as MaskProcessor. Now what MaskProcessor do? It is a high-performance word generator with a per-position configurable charset, which tries all combinations from a given keyspace just like in Brute-Force attack, but more specific. Then how it is different from brute-force attack?
MaskProcessor is Faster Than Brute-Force
The reason for doing this and not to stick to the traditional Brute-Force is that we want to reduce the password candidate keyspace to a more efficient one.
Here is a single example. We want to crack the password: Julia1984
In traditional Brute-Force attack we require a charset that contains all upper-case letters, all lower-case letters and all digits (aka “mixalpha-numeric”). The Password length is 9, so we have to iterate through 62^9 (13,537,086,546,263,552) combinations. Lets suppose we crack with a rate of 100M/s, this requires more than 4 years to complete.
In Mask attack we know about humans and how they design passwords. The above password matches a simple but common pattern. A name and year appended to it. We can also configure the attack to try the upper-case letters only on the first position. It is very uncommon to see an upper-case letter only in the second or the third position. To make it short, with Mask attack we can reduce the keyspace to 522626262610101010 (237,627,520,000) combinations. With the same cracking rate of 100M/s, this requires just 40 minutes to complete.
We can see the difference that how MaskProcessor can reduce our efforts. It just guessing the pattern of password and make a very shorter list for a quick job. There are some disadvantages are there also.
Disadvantage of MaskProcessor Compared to Brute-Force
There is none. We can argue that the above example is very specific but this does not matter. Even in mask attack we can configure our mask to use exactly the same keyspace as the Brute-Force attack does. The thing is just that this cannot work vice versa.
What are the Masks
For each position of the generated password candidates we need to configure a placeholder. If a password we want to crack has the length 8, our mask must consist of 8 placeholders.
- A mask is a simple string that configures the keyspace of the password candidate engine using placeholders.
- A placeholder can be either a custom charset variable, a built-in charset variable or a static letter.
- A variable is indicated by the ? letter followed by one of the built-in charset (l, u, d, s, a) or one of the custom charset variable names (1, 2, 3, 4).
- A static letter is not indicated by a letter. An exception is if we want the static letter ? itself, which must be written as ??.
Built-in character encoding
In MaskProcessor there are some built-in charsets. They are following:
- ?l = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
- ?u = ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
- ?d = 0123456789
- ?a = ?l?u?d?s
- ?b = 0x00 – 0xff
Not only these as we told in above that we can set custom charset in MaskProcessor.
Custom Charsets
There are four command-line-parameters to configure four custom charsets.
- –custom-charset1=CS
- –custom-charset2=CS
- –custom-charset3=CS
- –custom-charset4=CS
These command-line-parameters have four analogue shortcuts called -1, -2, -3 and -4. You can specify the chars directly on the command line.
Password Length Increment
A Mask attack is always specific to a password length. For example, if we use the mask ”?l?l?l?l?l?l?l?l” we can only crack a password of the length 8. But if the password we try to crack has the length 7 we will not find it. That’s why we have to repeat the attack several times, each time with one placeholder added to the mask. This is transparently automated by using the –increment flag.
- ?l
- ?l?l
- ?l?l?l
- ?l?l?l?l
- ?l?l?l?l?l
- ?l?l?l?l?l?l
- ?l?l?l?l?l?l?l
- ?l?l?l?l?l?l?l?l
Installing MaskProcessor on Kali Linux
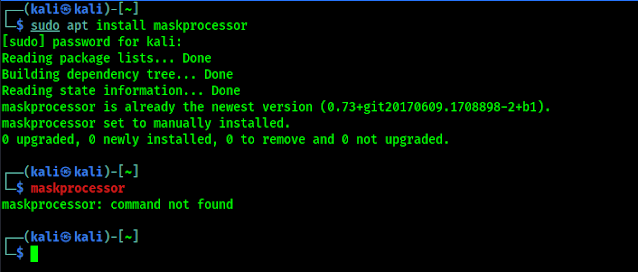
We can install a minimum version of MaskProcessor on our Kali Linux by using sudo apt install maskprocessor command. But there are some issue with this Kali Linux repository version. Like we had installed it but it is also saying ‘command not found’, as we can see in the following screenshot.
 |
|
MaskProcessor is installed but “command not found”
|
In this case we are going to uninstall this by using sudo apt remove maskprocessor command, and install it from scratch.
First we download it from it’s GitHub repository by using following command:
git clone https://github.com/hashcat/maskprocessor
Now MaskProcessor will be cloned on our system as we can see in the following screenshot:
Now we need to navigate into the maskprocessor/src directory by using following command:
cd maskprocessor/src
Here we build the program files by using the make command:
make
In the following screenshot we can see the output of the used command:
Now we move the mp64.bin file to /usr/bin directory and name it maskprocessor that it can be used as default tools. We can easily do it by using following command:
sudo mv ./mp64.bin /usr/bin/maskprocessor
Now our installation is complete. We can use MaskProcessor on our Kali Linux system. We can now use maskprocessor command to run it on our terminal.
Using MaskProcessor on Kali Linux
As we do always lets check MaskProcessor’s help options by applying following command on our terminal window:
maskprocessor -h
In the following screenshot we can see what we can do using MaskProcessor:
Now we learn how we can generate a specific wordlist in MaskProcessor. Here we need to know about the default charset as we told about in previous section, again mentioning here.
?l = abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
?u = ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
?d = 0123456789
?s = !”#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[]^_`{|}~
?a = ?l?u?d?s
?b = 0x00 – 0xff
All characters, except for those that stand for the set (?l, ?u, ?d, etc.), are included in the password unchanged. If we want to compose a dictionary that contains six-digit passwords we need to use maskprocessor ?d?d?d?d?d?d command but we also save the directory using -o flag. So our command will be as following:
maskprocessor ?d?d?d?d?d?d -o directory.txt
This will create a password directory named “directory.txt” which can break a six-digit password by brute-forcing attack.
Not only this. Almost every password-list creator tool can do this but MaskProcessor can do something better. Now we come into this point.
What if we know someone using a password which starts with voro followed by 4 numbers and then two capital letters. In this case we can easily create a password-list using MaskProcessor. We need to use following command:
maskprocessor voro?d?d?d?d?u?u -o passlist.txt
In the above command we have used voro then four ?d for four digits then two ?u for two capital letters, and bang it will create our required very special password list, as we can see in the following screenshot:
Bang!! Here is our special password list for cracking the specific password.
Now we can use MaskProcessor for creating special type of password lists. We can easily use MaskProcessor on our Kali Linux system.
HashCat vs MaskProcessor
Although, in general, MaskProcessor & Hashcat both are interchangeable to generate passwords, we need to remember that the -a 3 option must be specified to select the brute-force/mask attack mode (since Hashcat supports various attack modes, not only mask). We also need to use the –stdout option, which means to show the password candidates (without cracking the hash).
Hashcat (Mask attack) doesn’t allow us to set the maximum number of identical repeated characters, the maximum number of occurrences of one character, start or end at a specific position. But such a result can be obtained using a Rule-based attack.
Running Hashcat on Linux systems can be problematic due to the need to have proprietary drivers.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.














![[Easy] How to Install Brave Browser on Kali Linux [Easy] How to Install Brave Browser on Kali Linux](https://infocerts.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/How-to-Install-Brave-Browser-on-Kali-Linux-infocerts.jpg)