Maltego is one of the most famous OSINT frameworks for personal and organizational reconnaissance. It is a GUI tool that provides the capability of gathering information on any individuals, by extracting the information that is publicly available on the internet by diffrent methods. Maltego is also capable of enumerating the DNS, brute-forcing the normal DNS and collecting the data from social media in an easily readable format.
How are we going to use the Maltego in our goal-based penetration testing or red teaming exercise? We can utilize this tool in developing a visualization of data that we gathered. The community edition of Maltego comes with Kali Linux.
The tasks in Maltego are named as transforms. Transforms come built into the tool and are defined as being scripts of code that execute specific tasks. There are also multiple plugins available in Maltego, such as the SensePost toolset, Shodan, VirusTotal, ThreatMiner, and so on. Maltego offers the user with unprecedented information. Information is leverage. Information is power. Information is Maltego.
What does Maltego do?
Maltego is a program that can be used to determine the relationships and real world links between:
- People
- Groups of people (social networks)
- Companies
- Organizations
- Web sites
- Internet infrastructure such as:
- Domains
- DNS names
- Netblocks
- IP addresses
- Phrases
- Affiliations
- Documents and files
- These entities are linked using open source intelligence.
- Maltego is easy and quick to install – it uses Java, so it runs on Windows, Mac and Linux.
- Maltego provides you with a graphical interface that makes seeing these relationships instant and accurate – making it possible to see hidden connections.
- Using the graphical user interface (GUI) you can see relationships easily – even if they are three or four degrees of separation away.
- Maltego is unique because it uses a powerful, flexible framework that makes customizing possible. As such, Maltego can be adapted to your own, unique requirements.
What can Maltego do for us?
- Maltego can be used for the information gathering phase of all security related work. It will save our time and will allow you to work more accurately and smarter.
- Maltego aids us in your thinking process by visually demonstrating interconnected links between searched items.
- Maltego provide us with a much more powerful search, giving you smarter results.
- If access to “hidden” information determines your success, Maltego can help us discover it.
Setting Up Maltego on Kali Linux
The easiest way to access this application is to type maltego in our Terminal, also, we can open it from Kali Linux Application menu.
maltego
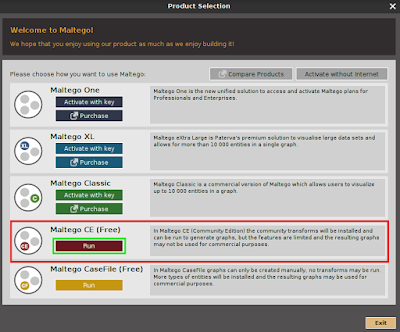
After first time we opened Maltego it will show us the product selection page, where we can buy various versions of Maltego, but the community edition of Maltego is free for everyone so we choose it (Maltego CE) and click on run, as shown in the following screenshot:
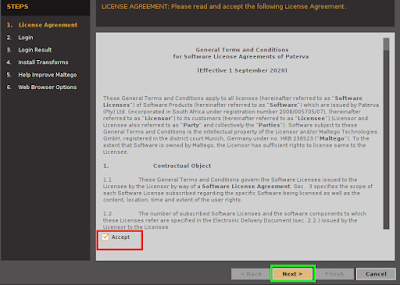
After clicking on “RUN”, we will got the configuring Maltego window. Here we need to login and setup our Maltego for the very first time. First we need to accept the terms and conditions of Maltego as we can see in the following screenshot:
On the above screenshot we can see that we check ✅ the “Accept” box and click on “Next”.
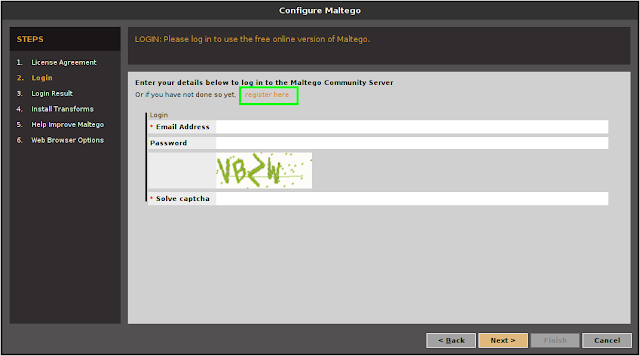
After that we got a login screen a we can see in the following screenshot:
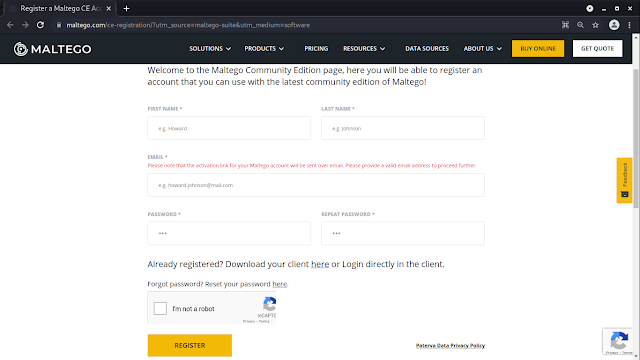
On the above screenshot we can see that note “LOGIN: Please log in to use the free online version of Maltego.” So, we need to log in here. But before that we need to Register to create our credential. We need to click on “Register”, and register page will open on our browser, or we can click here to go to the same page for register.
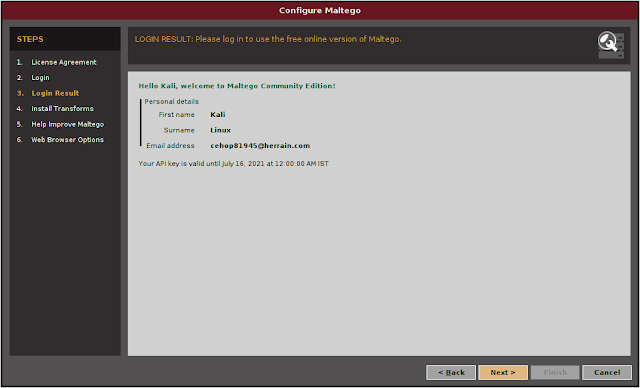
Here we need to fill up everything then they send activation link on our given mail address. For security reasons we are using temp-mail services, and we got our activation mail and activate it. After activating it we need to login from Maltego.
Then we just need to click “Next”, “Next”, “Next”, and our Maltego will open in front of us, as we can see in the following screenshot.
Running Maltego on Kali Linux
Now we are ready to use Maltego and run the machine, by navigating to “Machines” in the Menu folder and clicking on “Run Machine”; and then, we will be able to start an instance of the Maltego engine. Shown in the following screenshot:
After that we got a list of available options in Maltego public machines:
Usually, when we select Maltego Public Servers, we will have the following machine selections:
- Company Stalker: To get all email addresses at a domain and then see which one resolves on social networks. It also downloads and extracts metadata of the published documents on the internet.
- Find Wikipedia edits: This transform looks for the alias from the Wikipedia edits and searches for the same across all social media platforms.
- Footprint L1: Performs basic footprints of a domain.
- Footprint L2: Performs medium-level footprints of a domain.
- Footprint L3: Intense deep dive into a domain, typically used with care since it eats up all the resources.
- Footprint XXL: This works on the large targets such as a company hosting its own data centers, and tries to obtain the footprint by looking at sender policy framework (SPF) records hoping for netblocks, as well as reverse delegated DNS to their name servers.
- Person – Email Address: To obtain someone’s email address and see where it’s used on the internet. Input is not a domain, but rather a full email address.
- URL to Network and Domain Information: This transform will identify the domain information of other TLDs. For example, if we provide www.google.com, it will identify www.google.us, google.co.in, and so on and so forth.
Cybersecurity experts usually begin with “Footprint L1” to get a basic understanding of the domain and it’s potentially available sub-domains and relevant IP addresses. It is quite good to begin with this information as part of information gathering, however, pentesters can also utilize all the other machines as mentioned previously to achieve their goal.
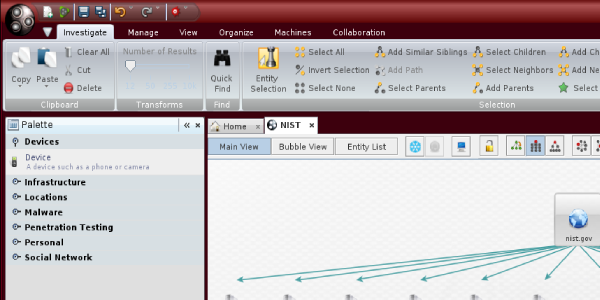
Once the machine is selected, we need to click on “Next” and specify a domain, for example google.com. The following screenshot provides the overview of google.com.
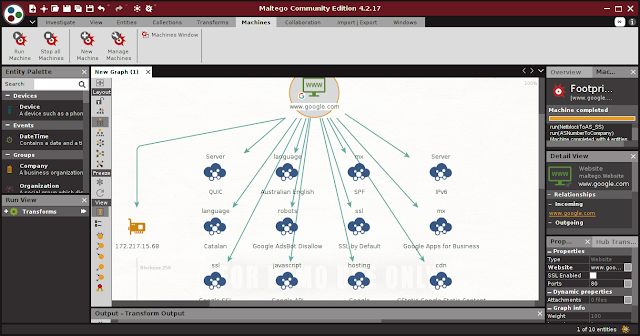 |
| Footprint L1 with Maltego on Google.com |
On the top-left side of the above screenshot, we will see the Palette window. In the Palette window, we can choose the entity type for which you want to gather the information. Maltego divides the entities into six groups as follows:
- Devices such as phone or camera.
- Infrastructure such as AS, DNS name, domain, IPv4 address, MX record, NS record, netblock, URL, and website.
- Locations on Earth.
- Penetration testing such as built with technology.
- Personal such as alias, document, e-mail address, image, person, phone number, and phrase.
- Social Network such as Facebook object, Twitter entity, Facebook affiliation, and Twitter affiliation.
If we right-click on the domain name, we will see all of the transforms that can be done to the domain name:
- DNS from domain.
- Domain owner’s details.
- E-mail addresses from domain.
- Files and documents from domain.
- Other transforms, such as To Person, To Phone numbers, and To Website.
- All transforms.
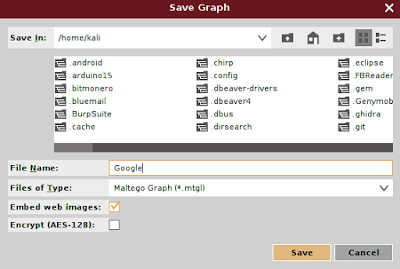
If we want to change the domain, you need to save the current graph first. To save the graph, click on the Maltego icon, and then select Save. The graph will be saved in the Maltego graph file format ( .mtgx ).
Then to change the domain, just double-click on the existing domain and change the domain name.
This is how Maltego works on our Kali Linux system. This is a very strong GUI based information gathering tool which comes loaded with Kali Linux.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxIn family, join our Telegram Group. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.




 ‘
‘