This article is about Categories of Security Challenges in Cloud Computing Virtualization.
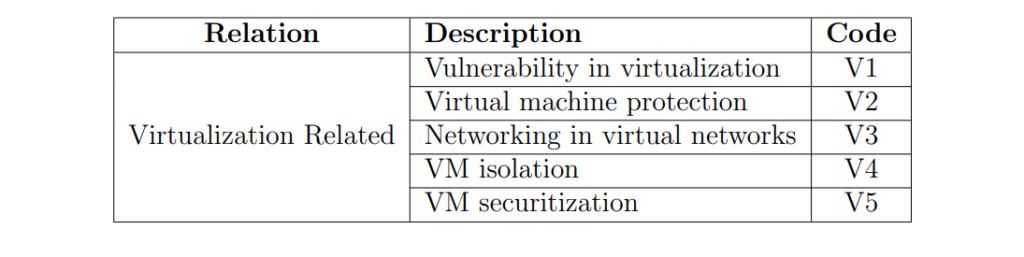
Vulnerability in Virtualization (V1)
Information from articles that discuss about vulnerability in virtualization and cross-vm information leakage are considered.
The most commonly used multiple way to create multiple virtual machines on a single physical machine is done using Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) approach. Hypervisors are also used to manage multiple VMs and any flaws in the hypervisors can allow attacker to gain access in an inappropriate way, even when tools such as Xen access are used many security risks can be found, which allow admin to see through the user level process while the customer is running his VM and attacker can easily install a malicious code [90][38][105]. In article [144][50] the author mentions that major risk is to ensure different instances running on the same physical machine are isolated and this requirement is not yet met completely. If virtual machines have vulnerabilities then sharing such hardware can result in many vulnerabilities [15]. To control and administer host, guest operating system is another issue which needs attention. The author also argues that most of the current existing systems do not satisfy perfect isolation and many bugs found here are from Virtual Machine Monitors (VMM’s). These bugs can be exploited by malicious local users and bypass some security restrictions or gain privileges. Ex., as been explained by the author “vulnerability in Xen caused due to an input
validation error in tools/pygrub/scr/GrubConf.py”, which can be exploited by ‘root’ users of a guest domain to execute arbitrary commands in a domain using specially designed entities in grub.conf (when guest is booted) [144][84][44][82]. If an unauthorized user hacks into CC, he can access all the virtual machines running in CC and control them [166]. Since CC is relatively cheap and provides resources to users easily and also since virtual machines (which is a main part of CC) are easy to copy or clone, the VMs can be easily used to launch new attacks
The following are some of the vulnerabilities by different authors mention in their work:
• Author for [134] mentions that trusted hypervisor is more important than having a trusted VM, because an untrusted hypervisor can affect to a greater extent.
• The author in [123] expresses that increased usage of virtualization is a Threat.
• In [50] the author mentions insecure areas in virtual machine which need to be secured and they are version management, customer specific application customization, migration between service providers, etc.
• An attacker can also cause damage to a cloud that is connected to a virtual machine by installing a bug in the source machine [126].
The above discussion makes clear that, if VM are not constantly monitored there can be service breakage [136].
Virtual machine protection (V2)
Information from articles that discuss about virtual machine protection and securing virtual machine boundaries are considered. Multiple VM’s can be instantiated or halted in a single server (machine) to satisfy list of services accepted. These services can also run multiple applications which are based on different operating system environments [25]. In relation to
this author in [6] expressed his concern towards securing the boundaries of virtual machines. Since the virtual machines created in cloud server have virtual boundaries (unlike general isolation where multiple hard disk drives), it’s the responsibility of CSP to ensure VM’s that use common resources on the same physical server (i.e., CPU, memory, I/O, NIC and others) are separated [6]. Also the host needs to be secure, because if the host is not secure protecting offline/online VMs is going to become a challenging task [38].
Virtualization in the cloud: The author expressed views on virtualization has been vulnerable to breaches, be it on traditional infrastructure or a Cloud architecture. This virtualization is a process of creating multiple Virtual Machines (VM’s), on a physical server to use a shared pool of resources, which also raises a concern on possibilities of spreading malicious activity. To prevent this kind of malicious activity in physical environment segmentation can be used, but in case of virtualized environment there is no possibility of segmenting. But without segmentation cloud could possibly allow hacker in web systems jump over to financial systems or databases. The solution to such kind of problem in virtual environments is to use Virtual Security Gateway, this enables users to apply some critical rules, log-in and access privileges, similar to what is done with systems placed in-house [3]. Supporting this author in [74] mentions that possibility that dynamically assigned virtual spaces in CC can already have some security threats.
Networking in virtual networks (V3)
Information from articles that discuss about networking in virtual networks, Networking problems, virtual management, virtual network security and hypervisor security are considered.
Virtual machine instances interconnectivity (i.e., communication) is a huge concern in CC [75][38]. Traditional mechanisms such as VLAN’s (Virtual Local Area Network) and firewalls are proving to be inefficient when used in a virtualized environment [73]. The security of a computer depends on the quality of underlying security mechanisms or kernels which control the execution of process [78]. Also when the devices are virtualized user might lose the visibility of how the VM’s are connected and insecure information transfer can be possible (information of one customer being disclosed to another customer) [163][138]. In addition to losing visibility, when considering security at the network level in virtual machines there arise two issues as discussed in article [6]. One of them is virtual network security, when sharing network infrastructure between different users within same server or physical network can increase possibility to exploit various vulnerabilities (DNS servers, DHCP, IP protocol, etc.) [6]. The other issue mentioned by [6], is on hypervisor security, this is the ‘virtualizer’ that links physical resources to virtualized resources and virtual machines in a virtual environment are given access to physical resources by this hypervisor. Hypervisor provides isolation
between the different guest and virtual machines. Since these hypervisors are virtual machines that run on physical machines and also smaller in comparison to physical systems, this helps in controlling and isolating processes. But now a days hypervisors or virtual machines are large, complex and comparable to an operating system [78]. Hence understanding hypervisor security is critical, any compromise on these machines can effect security of all users connected through it [6]. Examples of hypervisor software’s are VMware or Xen. Also the author in [56] mentions that the auto arrangement of virtual resources can Lead to problems and suggests that SPs need to perform security checks and constantly verify if user’s security requirements are met or not. One way to see that VMs are protected and not controlled by malicious users, administrators since they are the key persons in managing VM, the CSP should regulate the administrators from time to time [166]. Within most of virtualization platform existing there lies inbuilt ability, to create software based swatches and network configurations as part of the virtual environment and provide communication between virtual machines which is more efficient and direct. Traffic over virtual networks may not be visible to Security protection on physical networks, so there is a necessity to duplicate such services in virtual networks Some common attacks that can effect virtual machine’s network are “buffer overflow, DDoS, zero day attacks, viruses, covert channels, trojans, etc” mentioned, which can infect the hypervisor as it is the major VM controlling entity
VM isolation (V4)
Inter positioning is an inherent feature of VMM, isolation of VM is a key concern as it is not that possible CC and active inspection mechanisms are yet to be designed [73][75]. Multi-tenancy is a process where multiple cloud customers have their virtual instances running on the same physical server. In such environment, there might be a possibility for Malicious User allocating an instance in same the server and possibility is that he/she (malicious user) might penetrate the isolation between the VM’s and exploit them [128]. This could be possible by creating a side channel between two VM’s on a same physical machine and enabling a SSH keystroke timing outlined attack [34][141]. There is also a possibility that data accidentally crosses the virtual boundary [136]. The author in [126] mentions that even in an isolated environment if an attacker interferes with the VM placing strategy and position their instance on a physical machine of the victim, all the private information of target was visible.
To secure VMs, the VM instances need to be isolated, but at what level isolation should be Implemented i.e., is it at VM, physical machine, Local Area Network, VMM or at data centers [73]. The author in [105] mentions that logical separation need to be validated. Will that be sufficient? But there are more problems to handle.
Author in [38] mentions about protection from the interconnection of the VM, which connections are going into and which are coming out. The author explains various issues that can arise with existing technologies. The author [38] also mentioned there could be issues arising in the following areas of VM if isolation of VmM’s is not done properly by:
- Monitoring VMs from the host
- Communication between VM and host
- Monitoring Vm’s from other VM’s and virtual machines in mobility.
VM Securitization (V5)
Information from articles that discuss about VM securitization and VM security are considered.
VM introspection or behavioral monitoring in virtual machines requires a lot of computational power. It is easy to clone and distribute VM’s between physical servers but this distribution could result in propagation of configuration errors. Maintaining a hypervisor level, Media Access Control (MAC) and Trusted Computing techniques are suggested mechanisms used to build future secure cloud systems. In IaaS virtual machine security lies with the cloud consumer, a consumer can use their own security controls based on situation or security management process and expected risk level assessment [6].
——————————————————————————————————————–
Infocerts, 5B 306 Riverside Greens, Panvel, Raigad 410206 Maharashtra, India
Contact us – https://www.infocerts.com