In our some previous articles (Scalpel, Foremost etc) we have discussed how to can run digital forensics on hard disk drives. But data is not only stores there this included RAM and the swap partition, or paging, file, which is an area of the hard disk drive.
Now the issue is RAM’s data is very volatile, means the data in the RAM easily lost, when there are no electrical charge or current in the RAM chip. With the data on RAM being the most volatile, it ranks high in the order of volatility and must be forensically acquired and preserved as a matter of high priority.
Many types of data & forensics artifacts reside in Random Access Memory (RAM) and the paging file. They are might be login passwords, user information, running and hidden processes or even encrypted passwords are just some of the many types of interesting data that can be found when we run digital forensics test of RAM.
In our this article we use Volatility Framework to perform memory forensics on our Kali Linux system.
Volatility Framework is an open-source, cross-platform framework that comes with many useful plugins that provide us very good information from the snapshot of memory. This also known as memory dump.
The concept of Volatility is very old but it’s works like magic. Not only analyzing running and hidden processes, is also a very popular choice for malware analysis.
As we said Volatility Framework is a cross platform framework. It can be run on any OS (32 and 64 bit) that supports Python including:
- Windows XP, 7, 8,8.1, and Windows 10.
- Windows Server 2003, 2008, 2012/R2, and 2016.
- Linux 2.6.11 – 4.2.3 (including Kali, Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, and more).
- macOS Leopard (10.5.x) and Snow Leopard (10.12.x) and newer.
Volatility supports several memory dump formats (both 32- and 64-bit), including:
- Windows crash and hibernation dumps (even Windows 7 and earlier).
- VirtualBox.
- VMWare .vmem dump.
- VMware saved state and suspended dumps—.vmss/.vmsn.
- Raw physical memory—.dd.
- Direct physical memory dump over IEEE 1394 FireWire.
- Expert Witness Format (EWF)—.E01.
- QEMU (Quick Emulator).
Even we can convert between these formats and boosts of being able use Volatility with other tools.
Before use Volatility Framework we need to create a memory dump for testing. We can use several tools such as FTK imager, Helix, LiME can be used to acquire the memory image or memory dump. Then it can be investigated and analyzed by the Volatility Framework.
For this tutorial we are going to use a Windows XP image (named cridex.vmem) which is downloaded from here. Volatility have uploaded lots of memory samples publicly available for testing there. We can use them for our practice with the Volatility Framework and enhance our skills. We can download as many as we like and we can use various plugins available in Volatility. In the following screenshot we can see that our dump image is saved on our Desktop for easy access.
Using Volatility in Kali Linux
Volatility Framework comes pre-installed with full Kali Linux image. We can see the help menu of this by running following command:
volatility -h
Then we got the help of Volatility Framework as we can see in the following screenshot:
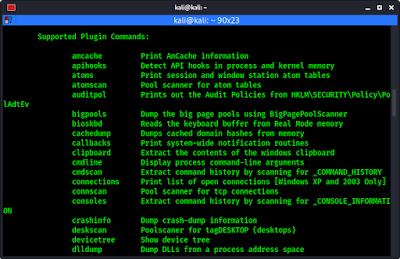
If we scroll down a little bit on the help menu we can find the list of all plugins within Volatility Framework.
This list comes in handy when performing analysis as each plugin comes with it’s own short description. In the following screenshot we can see a plugin with it’s description.
Gaining Information using Volatility
This imageinfo plugin will tell us about the image. The format for using plugins in Volatility is:
volatility -f [filename] [plugin] [options_if_required]
Now we have stored our image file on Desktop so first we change our working directory by using cd Desktop command. Then we run imageinfo plugin to check information of the image by applying following command:
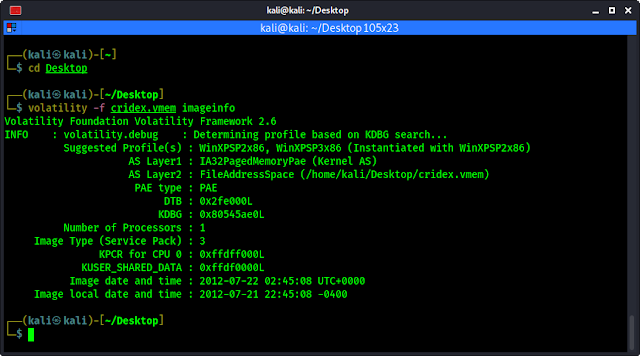
volatility -f cridex.vmem imageinfo
In the following screenshot we can see the information about our image file.
In the above screenshot we can see some information about the image used, including the suggested operating system and Image Type (Service Pack), the Numbers of Processor used and the date and time of the image. Some valuable information we got from this image is listed:
- WinXP: Windows XP.
- SP3: Service Pack 3.
- x86: 32 bit architecture.
We also can see the suggested profiles WinXPSP2x86 (Windows XP Service Pack 2×86), WinXPSP3x86 (Windows XP Service Pack 3×86) but in the image type section we can see that service pack is 3 so we can use “WinXPSP3x86” profile for our analysis.
Process Analysis using Volatility on Kali
To identify & link connected processes, their ID’s, running time and offset locations within the RAM image, we need these four plugins to get started:
- pslist
- pstree
- psscan
- psxview
1. Pslist Plugin on Volatility
This plugin or tool shows a list of all running processes, also it gives very crucial information like, Process ID (PID) and the Parent PID (PPID). Not only that it also shows the time when the processes started.
Let we run the pslist first then we explain the things. We use following command:
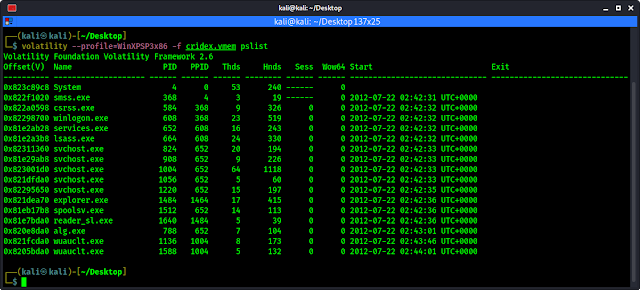
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem pslist
The following screenshot shows the output of the preceding command:
 |
| The Finding are discussed following |
In the above screenshot we can see the System, winlogon.exe, services.exe, svchost.exe, and explorer.exe services are all started first and then followed by reader_sl.exe, alg.exe, and finally wuauclt.exe.
The PID identifies the process and the PPID identifies the parent of the process. Looking at the pslist output, we can see that the winlogon.exe process has a PID of 608 and a PPID of 368. The PPID’s of the services.exe and the lsass.exe processes (directly after the winlogon.exe process) are both 608, indicating that winlogon.exe is in fact the PPID for both services.exe and lsass.exe.
For those new to process IDs and processes themselves, a quick Google search can assist with identification and description information. It is also useful to become familiar with many of the startup processes in order to readily point out processes that may be unusual or suspect.
The timing and order of the processes should also be noted as these may assist us in investigations. In the above screenshot, we can see that several processes, including explorer.exe, spoolsv.exe, and reader_sl.exe, all started at the same time of 02:42:36 UTC+0000. We can also tell that explorer.exe is the PPID of reader_sl.exe.
In this analysis, we can see that there are two instance of wuauclt.exe with svchost.exe as the PPID.
2. Pstree Plugin on Voltility
pstree is another process identification command that can be used to list processes. pstree shows output the same list of processes as the pslist command did in previous, but identification is also used to know which one child process and which one is parent process.
To run pstree we use following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem pstree
Following screenshot shows the output of the preceding command:
In the above screenshot, the last two processor listed are explorer.exe and reader_sl.exe. The explorer.exe is not indented, while reader_sl is indented, indicating that sl_reader is the child process and explorer.exe is the parent process. This is how we can identify the parent process and child process.
3. Psscan Plugin on Volatility
With the help of pslist and pstree we have checked the running processes, now it’s time look for inactive and even hidden processes using psscan. Now this hidden processes may be caused by malwares (like rootkits), and they are well known for doing just that to evade discovery by users & antivirus programs.
To check the inactive process using psscan we can use following command:
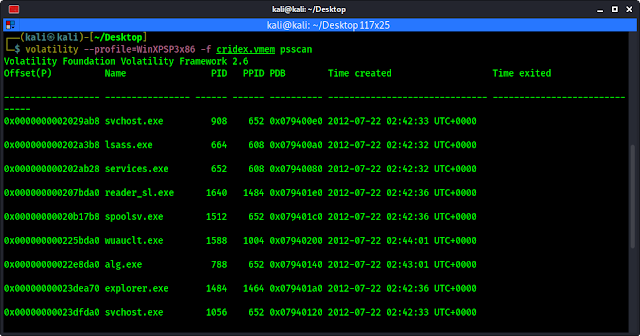
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem psscan
The output of the command shows in the following screenshot:
Now we can compare the outputs of both paslist and psscan to find any anomalies.
3. Psxview Plugin on Volatility
As with psscan, the psxview plugin is used to find and list hidden processes. With psxview however, a variety of scans are run, including pslist and psscan.
To run the psxview we apply following command:
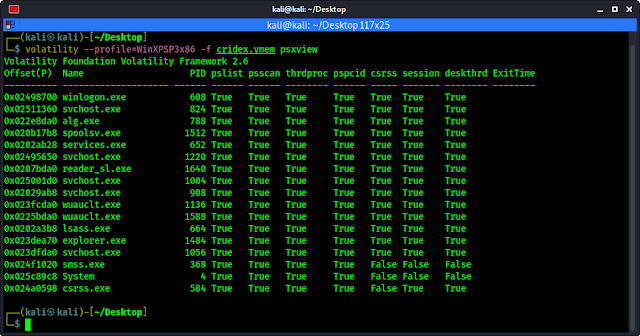
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem psxview
The output of the command shows in the following screenshot:
Analyzing Network Services & Connections using Volatility
Volatility can be used to find and analyze active, terminated, and hidden connections along with ports and processes. All the protocols are supported and Volatility also reveals details of ports used by the processes including the times the processes were started.
To do this we are going to use the following three commands:
- connections
- connscan
- sockets
1. Connection Plugin on Volatility
The connections command lists active connections at that time. It also displays local and remote IP with the ports and PID. The connection command can be used only for Windows XP and Microsoft 2003 server (both 32 bit and 64 bit).
To use the connections command in Volatility we can use following command:
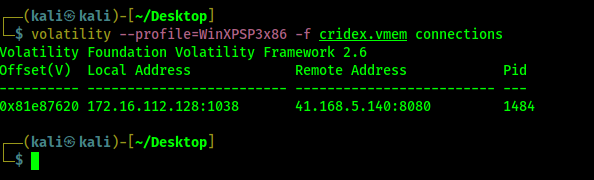
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem connections
The following screenshot shows the output of the connections command and we can see the IP address (both local and remote) along with the port numbers and PID.
2. Connscan Plugin on Volatility
The connections command displayed only on connection as active at that time. To see a list of connections that have been terminated, we can use the connscan command. This connscan command is also only for Windows XP and 2003 Server (both 32 bit and 64 bit) systems.
To use connscan we run the following command:
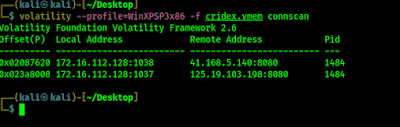
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem connscan
The screenshot of this command is following:
In the above screenshot we can see that same local address was previously connected to another Remote Address with the IP address 125.19.103.198 on port 8080. The PID of 1484 is proof that connection was made by the explorer.exe (tested on pslist earlier).
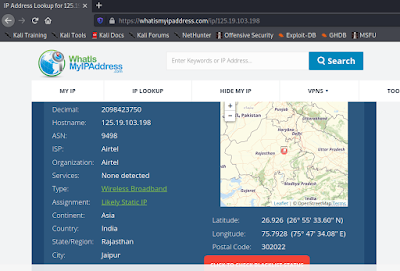
Here we got the Remote IP address. Now for more information we can search the IP address on some IP Look up web services like https://whatismyipaddress.com/ip-lookup or https://www.ip2location.com/demo. We got some additional information from there as we can see in the following screenshot.
We can get IP details like, ISP (Internet Service Provider) name, Continent, Country and City. We also got a map co-ordinate of the city.
3. Sockets Plugin on Volatility
We use the sockets plugin to give additional connectivity information listening sockets.
To use sockets plugin we can use following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem sockets
We can see the output of the command in the following screenshot:
We can see in the above that only UDP and TCP protocols are showing in this case. But sockets plugin supports all types of protocols.
Dynamic Link Libraries Analysis using Volatility
DDL a.k.a. Dynamic Link Libraries are only for Microfost (Windows & Servers). It contains code that can be used by multiple programs simultaneously.
Inspection of a process’s running DDLs and the version information of files and products may assist in correlating processes. Processes and DLL information should also be analyzed as they relate to the user accounts. For these tests we can use the following plugins:
- verinfo
- dlllist
- getsids
1. Verinfo plugin on Volatility
This plugin lists version information as we can see in the plugin name (verinfo) about PE (portable executable) files. The output of this file is usually quite lengthy and so can be run in a separate terminal, if we not wish to continuously scrool through the current terminal to review past plugin command lists and output.
We can use verinfo plugin by running following command:
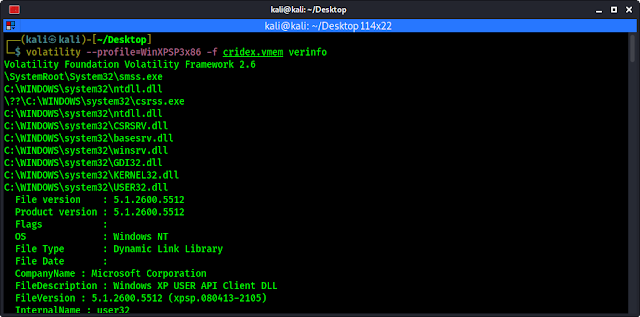
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem verinfo
The screenshot of the command is following:
2. Dlllist plugin on Volatility
This dlllist plugin lists all running DLLs at that time in memory. DLLs are composed of code that can be used by multiple programs concurrently.
We can use the dlllist plugin by running the following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem dlllist
The following screenshot shows the output of the command:
3. Getsids plugin on Volatility
To identify all users we can use Security Identifier (SID). The getsids command has four very useful items in the order in which the processes were started (refer to pslist and pstree command screenshots).
To run the getsids we can use following command:
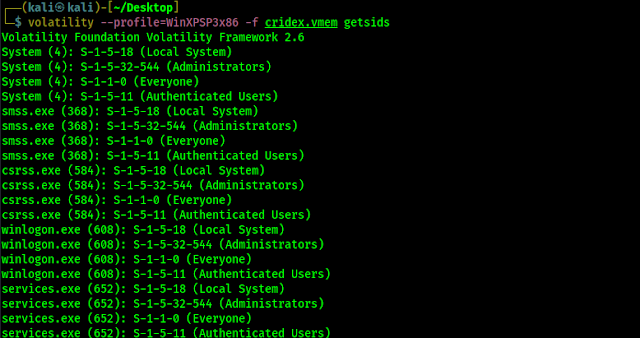
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem getsids
The screenshot of the command is following:
The format for the getsids plugin output is like following:
[Process] (PID) [SID] (User)
On the first line of the output we can see follwoing:
System (4): S-1-5-18 (Local System)
Here we explained in following bullets:
- Process : System
- PID : 4
- SID : S-1-5-18
- User : Local System
If the last number if SID is in a range of 500, that indicates the user with adminstratative privileges. For an example:
S-1-5-32-544 (Administrators)
Here we got something when we are scrolling down the getsids output, we can see that a user called Robert with an SID of S-1-5-21-789336058 (non-admin) has used started or accessed explorer.exe PID 1484.
Resgistry Analysis
Information about every users, settings, programs and the Windows operating system itself can be found within the registry. Even encrypted passwords can be found in the registry.
In the Windows registry analysis, we will be using the following two plugins.
- hivescan
- hivelist
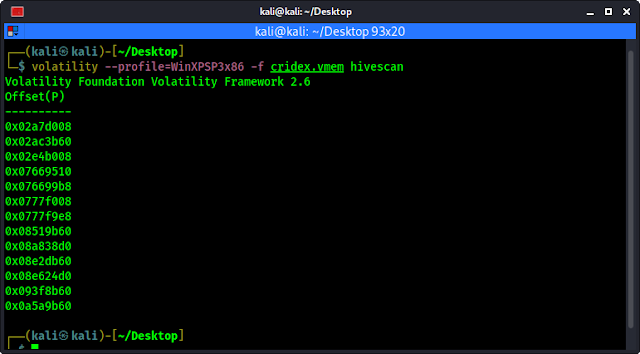
1. Hivescan plugin on Volatility
This hivesan plugin display the physical locations of available registry hives.
To use this plugin we need to run following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem hivescan
We can see the physical locations of available registry hives in the following screenshot:
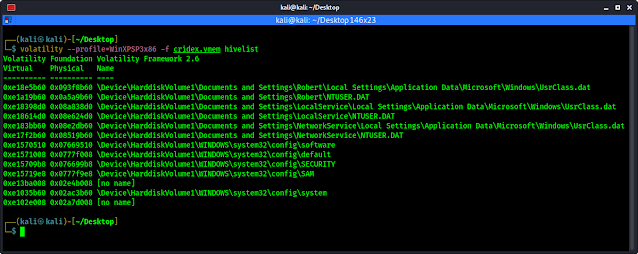
2. Hivelist plugin on Volatility
Hivelist plugin is used for more details (and helpful) information on registry hives and locations with RAM. This plugin shows the details of Virtual and Physical address along with the easier readable plaintext names and locations.
We use following command to run hivelist plugin on Volatility
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem hivelist
The output shows in the following screenshot:
In the above screenshot we can see information about vitual and physical address.
Password Dumping using Volatility
We know that Windows password stored on the SAM (Security Accounts Manager) file on Windows. This SAM file stores hashd passwords for usernames in Windows system. This file can’t be accessed by any user when the Windows system is on.
When we have used the hivelist command (previous screenshot) we have seen the SAM file if we carefully checked the output.
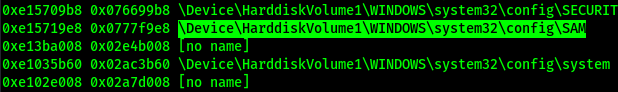 |
| We can see the SAM file during using hivelist plugin |
Timeline Investigation using Volatility
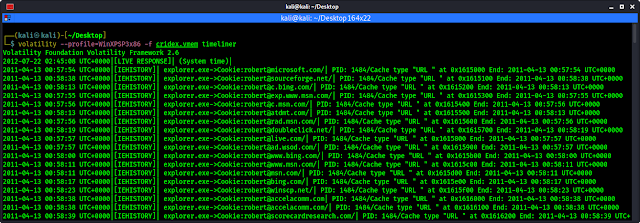
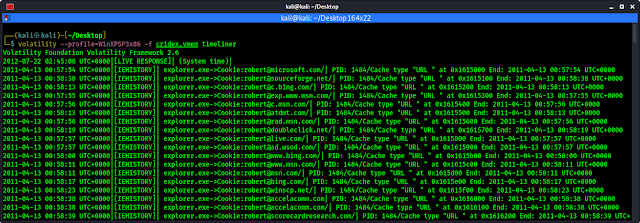
We can check timeline of all the events that took place when the image was acquired by using timeliner plugin on Volatility.
Although we have an idea of what took place within this scenario, many other dumps may be quite large and far more detailed and complex. The timeliner plugin will groups details by time and includes process, PID, process offser, DDLs used, registry details and other useful information.
To run timeliner command, we type the following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem timeliner
The output shows in the following screenshot:
This may produce long ouput and we need to scrool to see the full output.
Malware analysis
One of most important feature of Voatility is malfind plugin. This plugin is used to find, or at least direct us toward hints of malware that may have been injected into various processes.
The output of malfind plugin may be very lenghty so we should be run it in a separate terminal to avoid constant scrolling when reviewing the other plugin’s output.
The command used to run malfind pluin will be following:
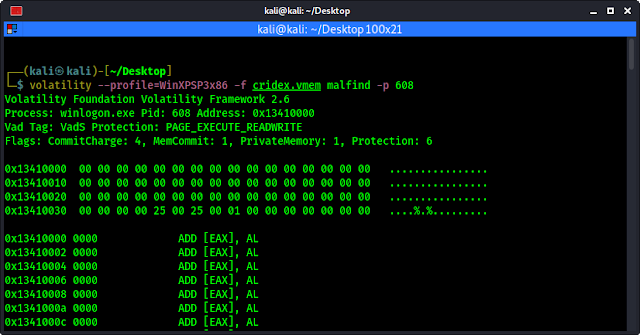
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem malfind
We can see the output on the following screenshot:
We can see a very long output here. To be more specific we can use -p flag to analyse a specific PID. As we have discovered previously (pslist plugin), winlogon.exe is assigned to PID 608. To analyze this specific PID in malfind we use following command:
volatility --profile=WinXPSP3x86 -f cridex.vmem malfind -p 608
The output of the command shown in the following screenshot:
Final Thoughts
In this article, we looked at memory forensics and analysis using some of the many plugins available within the Volatility Framework on our Kali Linux system.
One of the first, and most important, steps in working with Volatility is choosing the profile that Volatility will use throughout the analysis. This profile tells Volatility Framework what type of operating system is being used. Once the profile was chosen, we were able to successfully perform process, network, registry, DLL, and even malware analysis using this versatile framework.
As we’ve seen, Volatility can perform several important functions in digital forensics and should be used together with other tools we’ve used previously to perform in-depth and detailed forensic analysis and investigations.
Be sure to download more publicly available memory images and samples to test our skills in this area. Experiment with as many plugins as we can and of course, be sure to document our findings and consider sharing them online.
This is how we can perform Digital forensics on RAM and the swap partition etc using our Kali Linux system with the help of Volatility Framework.
Love our articles? Make sure to follow us on Twitter and GitHub, we post article updates there. To join our KaliLinuxInfamily, join our Telegram Group & Whatsapp Channel. We are trying to build a community for Linux and Cybersecurity. For anything we always happy to help everyone on the comment section. As we know our comment section is always open to everyone. We read each and every comment and we always reply.