This article is about security challenges in cloud computing with other concerns this is also one type of categories.
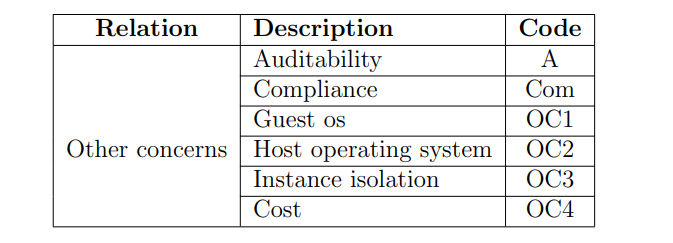
Auditability (A)
Information about auditability, audit and monitoring, audit and compliance, auditability and data, confidentiality, compliance and auditability from different articles are considered. Difficulty to audit is another side effect of cloud computing which shows, as there is lack of control in cloud [51]. Current auditing scheme in Cloud Computing goes on with the help of documentation or manual audits. Audit is an internal, external entity that organization implements to identify requirements that organization must abide with and helps to put into practice those policies, procedures and process which are needed to satisfy such requirements. Audit is also used to constantly keep checking if policies and principles are followed within organization or not. For organizations to use cloud computing platforms, cloud service providers (CSP) has to maintain, monitor and demonstrate on going compliance with customers business and regulatory requirements. Sustainability is not possible while maintaining separate efforts on different regulations or standards. Combination of internal policy, regulatory compliance and external auditing should be used When data is stored in remote locations auditing can become challenging or cost effective when doing it on site [7][126]. Also managing auditing is given as one of the 10 security management areas of Cloud Computing in [91]. Data confidentiality/auditability: Security is the most common area for critic by CC analysts, who keep asking “who would trust their essential data to be stored somewhere?”. Many cloud computing security threats are similar to those faced by data centers. This responsibility is divided among many parties such as vendor, cloud user and third party vendors that CC users depend in securing sensitive information. In cloud computing architecture user is responsible for his securing at application level; cloud service provider is responsible at physical level and enforcing firewall security. These responsibilities can also be outsourced and given to third party service providers who sell especially security services. Additional features such as firewall rule analysis can be provided by standardized interfaces of platforms such as Amazon EC2. With cloud computing, internal security threats are more when compared to external threats. Virtualization is key ingredient in cloud computing, with many benefits and at the same time it also brings numerous threats. Incorrect virtualization code might allow user to access sensitive portion of information of other user or provide access to service provider’s infrastructure. This all happens because virtualization software contains some bugs, which might allow virtualized code go loose to some extent. The service provider by default controls the software stack bottom layer which effectively circumvents most of the known security techniques.
A common problem that exists not only in case of cloud computing is, data lost into public and reason for this could be disposing a hard disk without being wiped or a bug within the program that makes data visible to unauthorized users partially.
Similarly, auditability could be added as an additional layer, which is kept out of reach for virtualized guest os, this provides arguably more security than those built into application. Such new features reinforce the cloud computing perspective of changing focus form specific hardware to virtualized capabilities [13][12]. In addition to all these mutual auditing should also be supported to cross check stakeholders in Cloud Computing [110]. It might be easy, or too easy to start using CC services but hard to govern cloud related activity.
Compliance (COM)
All the compliance related terms (such as compliance, regulatory compliance, audit and compliance) are identified from different articles are considered. Countries have their own security, privacy and regulatory laws at different levels (i.e., national, state and local), which makes compliance a complicated issue for cloud computing. Compliance requires conformance with the local established specifications, standards, regulations, or laws, which is hard for CC to demonstrate [135][78][92]. The customer must check if provider allows to timely audits, since customer is the one who is ultimately going to be responsible of data even when stored at SP [85]. The provider must allow customer to check if these through third party audits and also use preventive measures need to be employed for avoiding such violations [65][142][55][123]. Also the compliance can help the providers to restrict the customer from violating regulations that are agreed upon [109]. The author in [50] suggests to provide approaches for license management which ensure a compliant deployment of cloud resources.There are various issues discussed related, such as:
- Data location [78] (as discussed in subsection 4.2.1).
- Are service providers for cloud computing willing to support external audits and security certifications, similar to those of the traditional service providers [3].
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), is a set of comprehensive requirements for enhancing payment account data security and
this was developed by PCI Security Standards Council to adopt consistent data security measures on a global basis. This PCI DSS is a multifaceted security standard, which includes requirements for management of security, policies, procedures, network architecture, software design and other critical protective measures [3]. This is designed to protect customers account data. - Traditional service providers are allowed to external audits and security certifications. So, providers who refuse this are suggested to be used for only trivial functions [178][22].
- Virtualization and cloud computing have many issues that PCI Quality Assessors (PCI QA), have concerns about and it is necessary to show compliance to these rules, while deploying virtualization technology in PCI environment. Some of the important points to be noted are [3][28]:
a. Segregation of systems with one primary function per server and network with isolation of all management and control networks
b. Virtual media that contains cardholder data needs to be protected.
c. Support auditing on system components.
d. PCI DSS may require additional processes or technology to ensure patching and change control compliance in virtual environment.
e. Intrusion protection.
Guest operating system (OC1)
Generally an each customer in cloud is given a virtual private server (VPS), which can run any operating system requested by user in a physical machine.
This means multiple operating systems can be running in a physical machine and for a hacker find and trespass through any one of these operating systems running on VPS is not hard. Its the user responsibility to keep constantly patching up their own VM’s [105].
While interacting with CC services in some cases (where user is given complete virtual machine such as in IaaS) virtual instances are completely under control of customer. Amazon Web Services (AWS) does not give access to instances of customers and so cannot log into the guest OS [146].
Host operating system (OC2)
Administration hosts (build specifically to protect the management plane cloud) built to administer business needs in organization should be using multi-factor authentication before giving access. When an employee quits from job or has no longer access to the management plane, then his privileges should be revoked [46]. This is because if a malicious user gets access to the host he/she can effect the entire guest OS running in it which is a huge risk [105].
Instance isolation(OC3)
Instance isolation, Software isolation are different terms selected from primary selection and discussed here.
When user access a Cloud Computing service there is possibility for another user to be accessing same part of cloud or other part of it by creating its instance. Isolation is to ensure that different instances running on same physical machine remain isolated from each other. Since the administration of instances here is through instances but not direct, it increases the risk and possibility of threat to the security of Cloud Computing users. Hence, there needs to be efficient system control and access control restriction and a strict monitoring is needed to track changes. This isolation is efficient in Xen hypervisor and is being used by Amazon [46].
Cost (OC4)
Cloud computing applications can be easily used, but securing these applications requires management to spend additional resources (in terms of cash) [65]. Article [44] discusses multiple challenges and inter-relates their success of implementation to amount of cash an organization can spend.