This article is about Footprinting and Reconnaissance which comes under module 2 in Certified Ethical Hacker.
Reconnaissance refers to collecting information about a target, which is the first step in any attack on a system. It has its roots in military operations, where the term refers to the mission of collecting information about an enemy. Reconnaissance helps attackers narrow down the scope of their efforts and aids in the selection of weapons of attack. Attackers use the gathered information to create a blueprint, or “footprint,” of the organization, which helps them select the most effective strategy to compromise the system and network security.
Similarly, the security assessment of a system or network starts with the reconnaissance and footprinting of the target. Ethical hackers and penetration (pen) testers must collect enough information about the target of the evaluation before initiating assessments. Ethical hackers and pen testers should simulate all the steps that an attacker usually follows to obtain a fair idea of the security posture of the target organization. In this scenario, you work as an ethical hacker with a large organization. Your organization is alarmed at the news stories concerning new attack vectors plaguing large organizations around the world. Furthermore, your organization was the target of a major security breach in the past where the personal data of several of its customers were exposed to social networking sites.
You have been asked by senior managers to perform a proactive security assessment of the company. Before you can start any assessment, you should discuss and define the scope with management; the scope of the assessment identifies the systems, network, policies and procedures, human resources, and any other component of the system that requires security evaluation. You should also agree with management on rules of engagement (RoE) — the “do’s and don’ts” of assessment. Once you have the necessary approvals to perform ethical hacking, you should start gathering information about the target organization. Once you methodologically begin the footprinting process, you will obtain a blueprint of the security profile of the target organization. The term “blueprint” refers to the unique system profile of the target organization as the result of footprinting.
The labs in this module will give you a real-time experience in collecting a variety of information about the target organization from various open or publicly accessible sources.
Objective
The objective of the lab is to extract information about the target organization that includes, but is not limited to:
- Organization Information Employee details, addresses and contact details, partner details, weblinks, web technologies, patents, trademarks, etc.
- Network Information Domains, sub-domains, network blocks, network topologies, trusted routers, firewalls, IP addresses of the reachable systems, the Whois record, DNS records, and other related information
- System Information Operating systems, web server OSes, location of web servers, user accounts and passwords, etc.
Overview of Footprinting
Footprinting refers to the process of collecting information about a target network and its environment, which helps in evaluating the security posture of the target organization’s IT infrastructure. It also helps to identify the level of risk associated with the organization’s publicly accessible information.
Footprinting can be categorized into passive footprinting and active footprinting:
- Passive Footprinting: Involves gathering information without direct interaction. This type of footprinting is principally useful when there is a requirement that the information-gathering activities are not to be detected by the target.
- Active Footprinting: Involves gathering information with direct interaction. In active footprinting, the target may recognize the ongoing information gathering process, as we overtly interact with the target network.
Lab Tasks
Ethical hackers or pen testers use numerous tools and techniques to collect information about the target. Recommended labs that will assist you in learning various footprinting techniques include:
- Perform footprinting through search engines
- Gather information using advanced Google hacking techniques
- Gather information from video search engines
- Gather information from FTP search engines
- Gather information from IoT search engines
- Perform footprinting through web services
- Find the company’s domains and sub-domains using Netcraft
- Gather personal information using PeekYou online people search service
- Gather an email list using theHarvester
- Gather information using deep and dark web searching
- Determine target OS through passive footprinting
- Perform footprinting through social networking sites
- Gather employees’ information from LinkedIn using theHarvester
- Gather personal information from various social networking sites using Sherlock
- Gather information using Followerwonk
- Perform website footprinting
- Gather information about a target website using ping command line utility
- Gather information about a target website using Photon
- Gather information about a target website using Central Ops
- Extract a company’s data using Web Data Extractor
- Mirror a target website using HTTrack Web Site Copier
- Gather information about a target website using GRecon
- Gather a wordlist from the target website using CeWL
- Perform email footprinting
- Gather information about a target by tracing emails using eMailTrackerPro
- Perform Whois footprinting
- Perform Whois lookup using DomainTools
- Perform DNS footprinting
- Gather DNS information using nslookup command line utility and online tool
- Perform reverse DNS lookup using reverse IP domain check and DNSRecon
- Gather information of subdomain and DNS records using SecurityTrails
- Perform network footprinting
- Locate the network range
- Perform network tracerouting in Windows and Linux Machines
- Perform footprinting using various footprinting tools
- Footprinting a target using Recon-ng
- Footprinting a target using Maltego
- Footprinting a target using OSRFramework
- Footprinting a target using FOCA
- Footprinting a target using BillCipher
- Footprinting a target using OSINT Framework
Lab 1: Perform Footprinting Through Search Engines
Lab Scenario
As a professional ethical hacker or pen tester, your first step is to gather maximum information about the target organization by performing footprinting using search engines; you can perform advanced image searches, reverse image searches, advanced video searches, etc. Through the effective use of search engines, you can extract critical information about a target organization such as technology platforms, employee details, login pages, intranet portals, contact details, etc., which will help you in performing social engineering and other types of advanced system attacks.
Lab Objectives
- Gather information using advanced Google hacking techniques
- Gather information from video search engines
- Gather information from FTP search engines
- Gather information from IoT search engines
Overview of Search Engines
Search engines use crawlers, automated software that continuously scans active websites, and add the retrieved results to the search engine index, which is further stored in a huge database. When a user queries a search engine index, it returns a list of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). These results include web pages, videos, images, and many different file types ranked and displayed based on their relevance. Examples of major search engines include Google, Bing, Yahoo, Ask, Aol, Baidu, WolframAlpha, and DuckDuckGo.
Task 1: Gather Information using Advanced Google Hacking Techniques
Advanced Google hacking refers to the art of creating complex search engine queries by employing advanced Google operators to extract sensitive or hidden information about a target company from the Google search results. This can provide information about websites that are vulnerable to exploitation.
Note: Here, we will consider EC-Council as a target organization. However, you can select a target organization of your choice.
- Click CEHv12 Windows 11 to switch to the Windows 11 machine, click Ctrl+Alt+Del.
- By default, Admin user profile is selected, type Pa$$w0rd in the Password field and press Enter to login.
- Note: If Welcome to Windows wizard appears, click Continue and in Sign in with Microsoft wizard, click Cancel.
- Note: Networks screen appears, click Yes to allow your PC to be discoverable by other PCs and devices on the network.

- Launch any browser, in this lab we are using Mozilla Firefox. In the address bar of the browser place your mouse cursor and type https://www.google.com and press Enter.
- Note:
- If the Default Browser pop-up window appears, uncheck the Always perform this check when starting Firefox checkbox and click the Not now button.
- If a notification appears, click Okay, Got it to finish viewing the information.
- Once the Google search engine appears, you should see a search bar.
- Note: If any pop-up window appears at the top-right corner, click No thanks.

- Type intitle:login site:eccouncil.org and press Enter. This search command uses intitle and site Google advanced operators, which restrict results to pages on the eccouncil.org website that contain the login pages. An example is shown in the screenshot below.
- Note: Here, this Advanced Google Search operator can help attackers and pen testers to extract login pages of the target organization’s website. Attackers can subject login pages to various attacks such as credential bruteforcing, injection attacks and other web application attacks. Similarly, assessing the login pages against various attacks is crucial for penetration testing.

- Now, click back icon present on the top-left corner of the browser window to navigate back to https://www.google.com.

- In the search bar, type the command EC-Council filetype:pdf and press Enter to search your results based on the file extension.
- Note: Here, the file type pdf is searched for the target organization EC-Council. The result might differ when you perform this task.
- Note: The PDF and other documents from a target website may provide sensitive information about the target’s products and services. They may help attackers to determine an attack vector to exploit the target.

- Now, click on any link from the results (here, first link) to view the pdf file.

- The page appears displaying the PDF file, as shown in the screenshot.

- Apart from the aforementioned advanced Google operators, you can also use the following to perform an advanced search to gather more information about the target organization from publicly available sources.
- cache: This operator allows you to view cached version of the web page. [cache:www.eccouncil.org]- Query returns the cached version of the website www.eccouncil.org
- allinurl: This operator restricts results to pages containing all the query terms specified in the URL. [allinurl: EC-Council career] — Query returns only pages containing the words “EC-Council” and “career” in the URL
- inurl: This operator restricts the results to pages containing the word specified in the URL [inurl: copy site:www.eccouncil.org]—Query returns only pages in EC-Council site in which the URL has the word “copy”
- allintitle: This operator restricts results to pages containing all the query terms specified in the title. [allintitle: detect malware] — Query returns only pages containing the words “detect” and “malware” in the title
- inanchor: This operator restricts results to pages containing the query terms specified in the anchor text on links to the page. [Anti-virus inanchor:Norton] — Query returns only pages with anchor text on links to the pages containing the word “Norton” and the page containing the word “Anti-virus”
- allinanchor: This operator restricts results to pages containing all query terms specified in the anchor text on links to the page. [allinanchor: best cloud service provider] — Query returns only pages in which the anchor text on links to the pages contain the words “best,” “cloud,” “service,” and “provider”
- link: This operator searches websites or pages that contain links to the specified website or page. [link:www.eccouncil.org]—Finds pages that point to EC-Council’s home page
- related: This operator displays websites that are similar or related to the URL specified. [related:www.eccouncil.org]—Query provides the Google search engine results page with websites similar to eccouncil.org
- info: This operator finds information for the specified web page. [info:eccouncil.org] — Query provides information about the www.eccouncil.org home page
- location: This operator finds information for a specific location. [location: EC-Council] — Query give you results based around the term EC-Council
- This concludes the demonstration of gathering information using advanced Google hacking techniques. You can conduct a series of queries on your own by using these advanced Google operators and gather the relevant information about the target organization.
- Close all open windows and document all the acquired information.
Task 2: Gather Information from Video Search Engines
Video search engines are Internet-based search engines that crawl the web looking for video content. These search engines either provide the functionality of uploading and hosting the video content on their own web servers or they can parse the video content, which is hosted externally.
Here, we will perform an advanced video search and reverse image search using the YouTube search engine and YouTube Metadata tool.
Note: Here, we will consider EC-Council as a target organization. However, you can select a target organization of your choice.
- Launch any browser, in this lab we are using Mozilla Firefox. In the address bar of the browser place your mouse cursor and type https://www.youtube.com and press Enter. YouTube page appears as shown in the screenshot.
- Note: If you choose to use another web browser, the screenshots will differ.

- In the search field, search for your target organization (here, ec-council). You will see all the latest videos uploaded by the target organization.
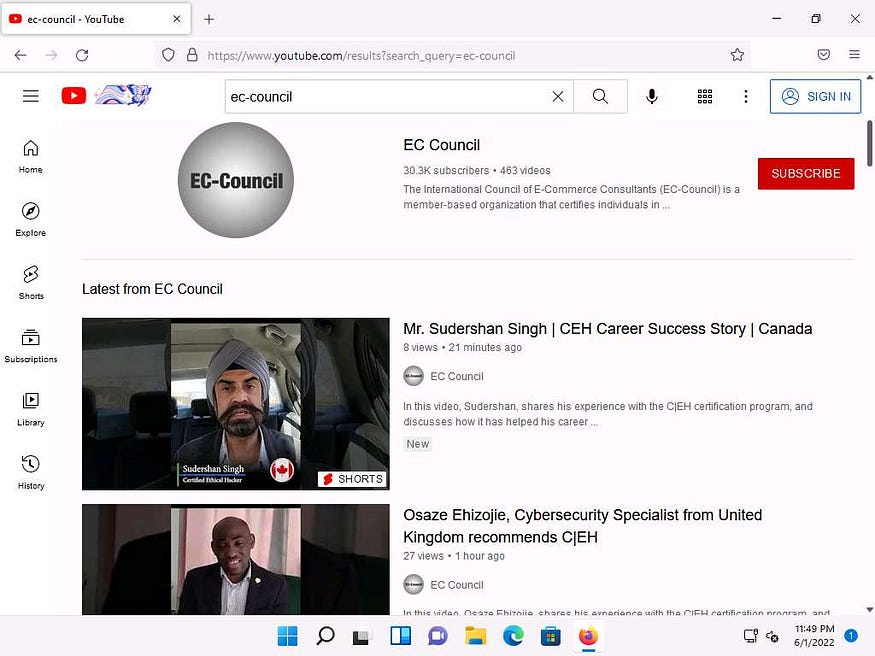
- Select any video of your choice, right-click on the video title, and click Copy Link.
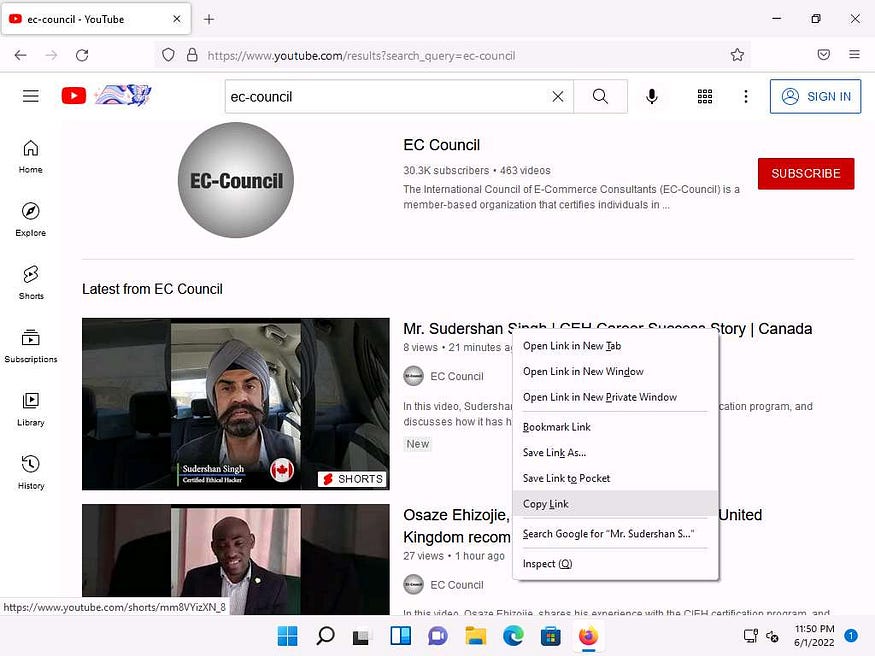
- After the video link is copied, open a new tab in Mozilla Firefox, place your mouse cursor in the address bar and type **https://mattw.io/youtube-metadata/ ** and press Enter.
- Note: To open a new tab, click + icon next to the first tab.
- Note: YouTube Metadata tool collects singular details of a video, its uploader, playlist and its creator or channel.

- YouTube Metadata page appears, in the Submit a link to a video, playlist, or channel search field, paste the copied YouTube video location and click Submit.

- Once the search is completed scroll down and you can observe the details related to the video such as published date and time, channel Id, title, etc., in the Snippet section.

- Scroll down to check the additional information under the sections Statistics, Geolocation , and Status etc.

- Under the Thumbnail section you can find the reverse image search results, click on the Click to reverse image search button under any thumbnail.
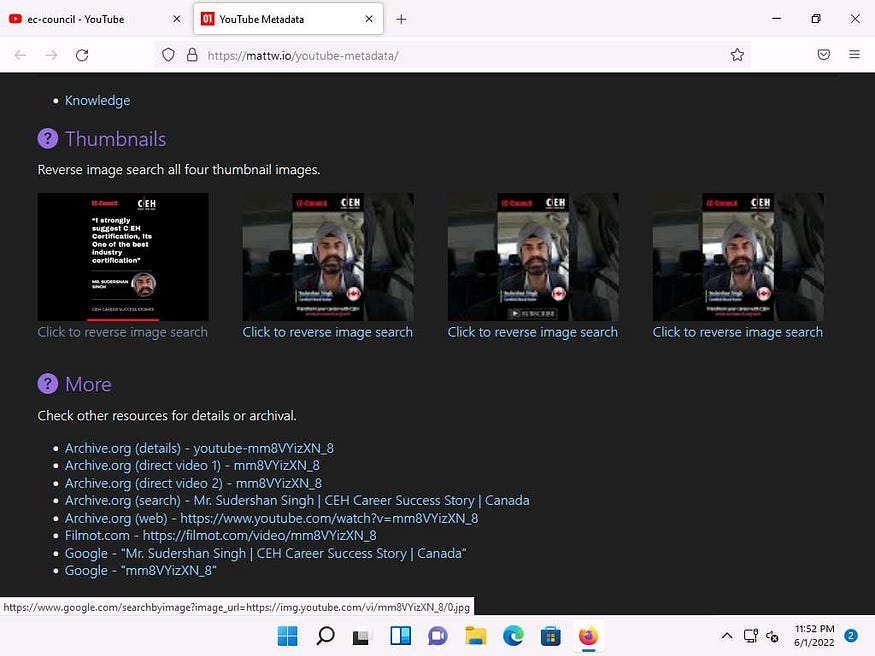
- A new tab in Google appears, and the results for the reverse image search are displayed.

- This concludes the demonstration of gathering information from the advanced video search and reverse image search using the YouTube search engine and YouTube Metadata tool.
- You can use other video search engines such as Google videos (https://www.google.com/videohp), Yahoo videos (https://in.video.search.yahoo.com), etc.; video analysis tools such as EZGif (https://ezgif.com), VideoReverser.com (https://www.videoreverser.com) etc.; and reverse image search tools such as TinEye Reverse Image Search (https://tineye.com), Yahoo Image Search (https://images.search.yahoo.com), etc. to gather crucial information about the target organization.
- Close all open windows and document all acquired information.

