The twentieth century U.S. criminal Willie Sutton was said to rob banks because “that’s where the money is.” The same motivation in our digital age makes merchants the new target for financial fraud. Occasionally lax security by some merchants enables criminals to easily steal and use personal consumer
financial information from payment card transactions and processing systems. It’s a serious problem – more than 10.9 billion records with sensitive information have been breached according to public disclosures between January 2005 and July 2018, according to PrivacyRights.org. As you are a key participant in payment card transactions, it is imperative that you use standard security procedures and technologies to thwart theft of cardholder data.
Merchant-based vulnerabilities may appear almost anywhere in the card-processing ecosystem including:
• point-of-sale devices;
• mobile devices, personal computers or servers;
• wireless hotspots;
• web shopping applications;
• paper-based storage systems;
• the transmission of cardholder data to service providers;
• in remote access connections.
Vulnerabilities may also extend to systems operated by service providers and acquirers, which are the financial institutions that initiate and maintain the relationships with merchants that accept payment cards (see diagram on page 5).
Compliance with the PCI DSS helps to alleviate these vulnerabilities and protect cardholder data.

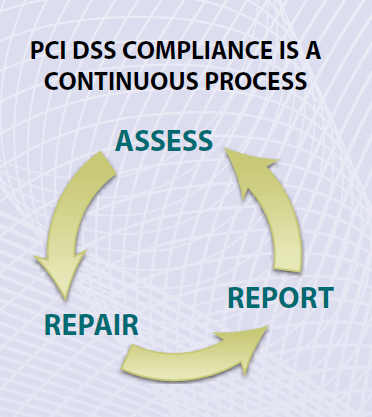
The intent of this PCI DSS Quick Reference Guide is to help you understand how the PCI DSS can help protect your payment card transaction environment and how to apply it. There are three ongoing steps for adhering to the PCI Dss: Assess — identifying all locations of cardholder data, taking an inventory of your IT assets and business processes for payment card processing and analyzing them for vulnerabilities that could expose cardholder data.
Repair — fixing identified vulnerabilities, securely removing any unnecessary cardholder data storage, and implementing secure business processes.
Report — documenting assessment and remediation details, and submitting compliance reports to the acquiring bank and card brands you do business with (or other requesting entity if you’re a service provider). PCI DSS follows common-sense steps that mirror security best practices. The PCI DSS globally applies to all entities that store, process or transmit cardholder data and/or sensitive authentication data. PCI DSS and related security standards are administered by the PCI Security Standards Council, which was founded by American Express, Discover Financial Services, JCB International, MasterCard Worldwide and Visa Inc.
Participating Organizations include merchants, payment card issuing banks, processors, developers and other vendors.
Overview of PCI Requirements
PCI Security Standards are technical and operational requirements set by the PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) to protect cardholder data. The standards apply to all entities that store, process or transmit cardholder data – with requirements for software developers and manufacturers of applications and devices used in those transactions. The Council is responsible for managing the security standards, while compliance with the PCI set of standards is enforced by the founding members of the Council: American Express, Discover Financial Services, JCB, MasterCard and Visa Inc.
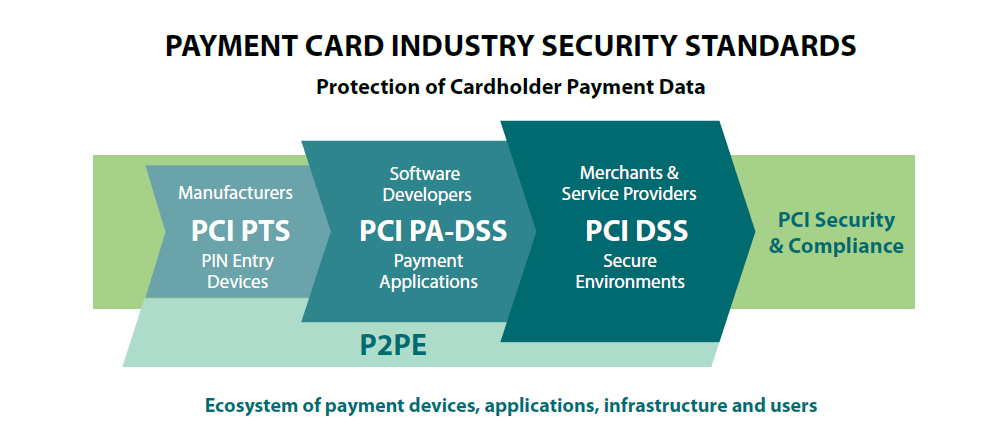
PCI Security Standards Include:
PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The PCI DSS applies to all entities that store, process, and/or transmit cardholder data. It covers technical and operational system components included in or connected to cardholder data. If you accept or process payment cards, PCI DSS applies to you.
PIN Transaction Security (PTS) Requirements
The PCI PTS is a set of security requirements focused on characteristics and management of devices used in the protection of cardholder PINs and other payment processing related activities. The PTS standards include PIN Security Requirements, Point of Interaction (POI) Modular Security Requirements, and Hardware Security Module (HSM) Security Requirements. The device requirements are for manufacturers to follow in the design, manufacture and transport of a device to the entity that implements it. Financial institutions, processors, merchants and service providers should only use devices or components that are tested and approved by the PCI SSC, listed at: www.pcisecuritystandards.org/assessors_and_solutions/pin_transaction_devices.
Payment Application Data Security Standard (PA-DSS)
The PA-DSS is for software vendors and others who develop payment applications that store, process or transmit cardholder data and/or sensitive authentication data as part of authorization or settlement, when these applications are sold, distributed or licensed to third parties. Most card brands encourage merchants to use payment applications that are tested and approved by the PCI SSC.
Validated applications are listed at: www.pcisecuritystandards.org/assessors_and_solutions/payment_applications.
PCI Point-to-Point Encryption Standard (P2PE)
This Point-to-Point Encryption (P2PE) standard provides a comprehensive set of security requirements for P2PE solution providers to validate their P2PE solutions, and may help reduce the PCI DSS scope of merchants using such solutions. P2PE is a cross-functional program that results in validated solutions incorporating the PTS Standards, PA-DSS, PCI DSS, and the PCI PIN Security Standard. Validated P2PE solutions are listed at: www.pcisecuritystandards.org/assessors_and_solutions/point_to_point_encryption_solutions.
PCI Card Production Logical Security Requirements and Physical Security Requirements
The Card Production Logical and Physical Security Requirements address card production activities including card manufacturing, chip embedding, data preparation, pre-personalization, card personalization, chip personalization, fulfillment, packaging, storage, mailing, shipping, PIN printing and mailing (personalized, credit or debit), PIN printing (non-personalized prepaid cards), and electronic PIN distribution.
PCI Token Service Provider Security Requirements
The Token Service Provider (TSP) Security Requirements are intended for Token Service Providers that generate and issue EMV Payment Tokens, as defined under the EMV® Payment Tokenization Specification Technical Framework.
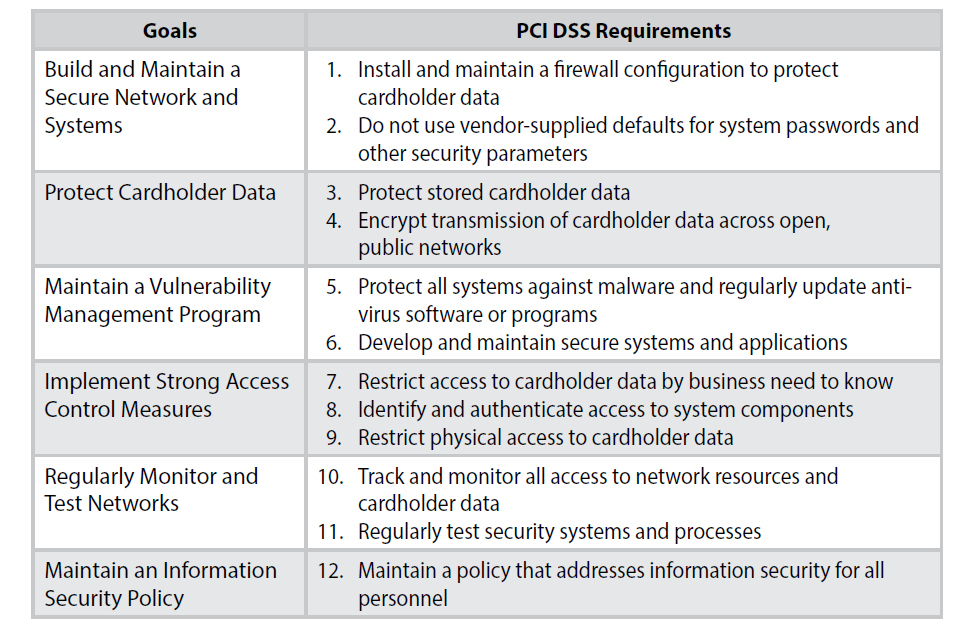
The PCI Data Security Standard
PCI DSS is the global data security standard adopted by the payment card brands for all entities that process, store or transmit cardholder data and/or sensitive authentication data. It consists of steps that mirror security best practices.
The PCI SSC sets the PCI Security Standards, but each payment card brand has its own program for compliance, validation levels and enforcement. For more information about compliance programs, contact the payment brands or your acquiring bank.
Qualified Assessors. The Council manages programs that will help facilitate the assessment of compliance with PCI DSS: Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) and Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV). QSAs are approved by the Council to assess compliance with the PCI DSS. ASVs are approved by the Council to validate adherence to the PCI DSS scan requirements by performing vulnerability scans of Internet-facing environments of merchants and service providers. The Council also provides PCI DSS training for Internal Security Assessors (ISAs). Additional details can be found on our website at:
www.pcisecuritystandards.org/approved_companies_providers/index.php.
Self-Assessment Questionnaire. The Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) is a validation tool for eligible organizations who self-assess their PCI DSS compliance and who are not required to submit a Report on Compliance (ROC). Different SAQs are available for various business environments; more details can be found on our website at: www.pcisecuritystandards.org/document_library?category=saqs#. To determine whether you should complete a SAQ (and if so, which one),contact your organization’s acquiring financial institution or payment card brand.
People also ask this Questions
- What is a defense in depth security strategy how is it implemented?
- What is AWS Solution Architect?
- What is the role of AWS Solution Architect?
- Is AWS Solution Architect easy?
- What is AWS associate solutions architect?
- Is AWS Solutions Architect Associate exam hard?
Infocerts, 5B 306 Riverside Greens, Panvel, Raigad 410206 Maharashtra, India
Contact us – https://www.infocerts.com


